- Home
- Data Visualization
- Tools
- AI Data Analyst
- Excel Formula Generator
- Excel Formula Explainer
- Google Apps Script Generator
- Excel VBA Script Explainer
- Excel VBA Script Generator
- Excel VBA Code Optimizer
- Excel VBA Code Debugger
- Google Sheets Formula Generator
- Google Apps Script Explainer
- Google Sheets Formula Explainer
- Google Apps Script Optimizer
- Google Apps Script Debugger
- Excel File Translator
- Excel Template Generator
- Excel Add-in
- Your Virtual AI Assistant For Excel Spreadsheets
- AI Answer Generator
- AI Math Solver
- AI Graph Generator
- AI SQL Generator
- Pricing
- Resources
Explore other articles
- Top 5 Julius AI Alternatives for Data Analysis in 2025
- No Code Analytics: Business Impact and Top Tools in 2025
- Top Automation Tools for Excel in 2025: Built-In and Third-Party Solutions
- 5 Healthcare Data Analytics Trends 2025
- Which is the Best Analytics Platform for Startup Data Needs in 2025
- 10 Must-Have AI Tools for Startups in 2025
- 7 Best AI Tools for Excel Data Analysis (2025 Comparison)
- Why is AI-driven Data Intelligence the Key to Success?
- The Essential Role of AI in Conversational Analytics
- Which AI Model Will Survive Our Test: Claude vs Perplexity?
The ability to transform numbers into clear and insightful stories is more important than ever. Data visualization is the key to unlocking these stories, but with so many charts and graphs, how do you know which best represents your information?
This guide dives into the core data visualization principles, providing real-world examples to illustrate choosing the right chart type, using color effectively, and designing dashboards that resonate with your audience.
Looking to create reporting system fast & painlessly?
Build dashboards and track KPIs in one place with Ajelix BI
Role Of Data Visualization
Data visualization is the graphical representation of data. It transforms complex data into understandable visuals, making identifying patterns, trends, and outliers easier. It plays a crucial role in various fields, including Business and Analytics, Science and Research, Journalism and Storytelling, and other roles.
Our brains process visual information faster and more intuitively than text. It bridges the gap between raw numbers and human comprehension, helping individuals and organizations harness the power of data effectively.
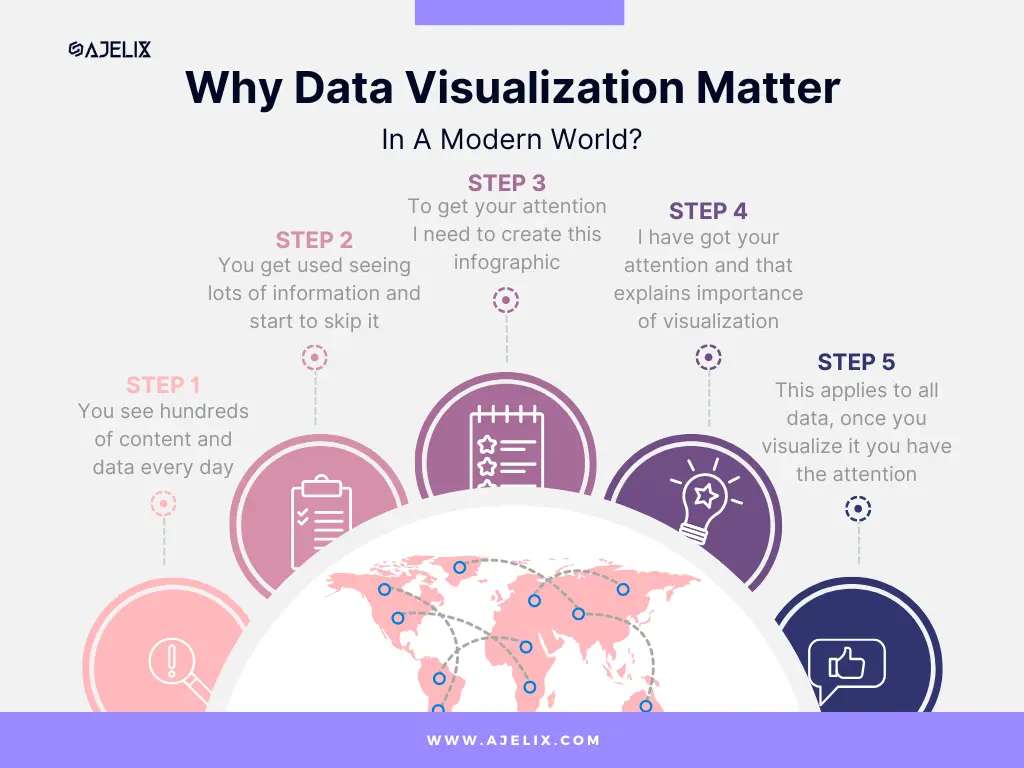
Here’s an example of how data visualization works:
- You see hundreds of content every day
- You get used to seeing lots of information and start to skip it
- To get your attention I have to create an infographic
- I have got your attention and that explains the importance of visualization
A great resource to understand data visualization in more detail is the book Data Visualization: Principles and Practice, Second Edition
How Visualization Improves Data Understanding and Decision-Making
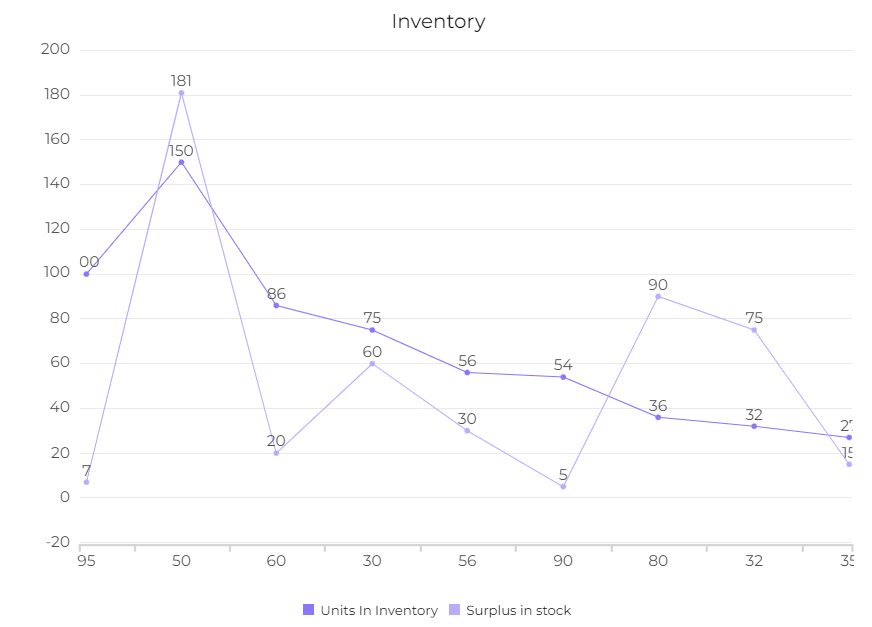
Visualizations provide a roadmap through the numbers complex landscape. It simplifies the information, allowing us to extract insights swiftly. Here’s an example of how representing the same data within the table vs chart you can make better decisions.
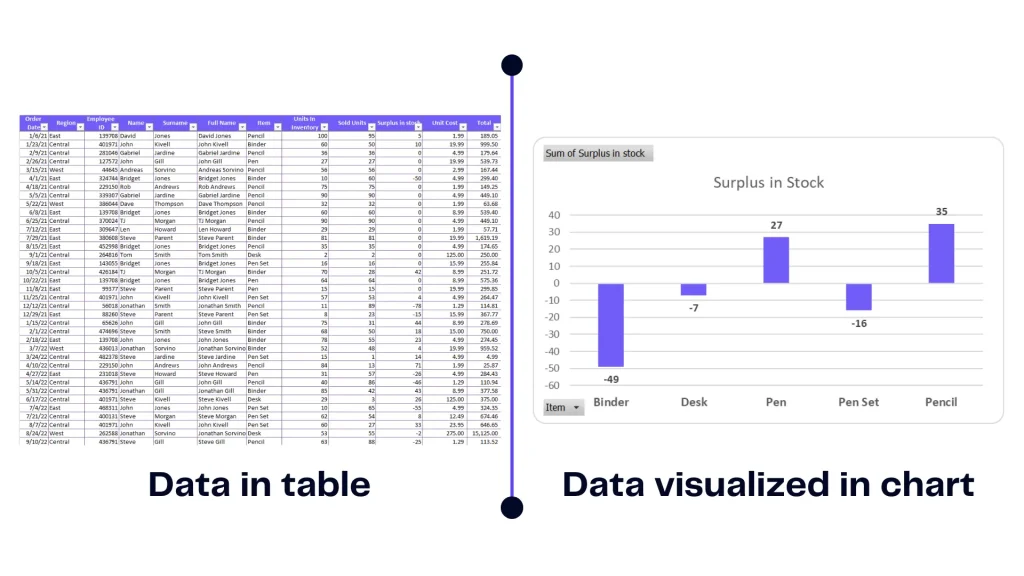
Infographic emphasizing the importance of visualization, image by author
This example enlarges the importance of visualization as you can’t make decisions from a table. You simply can’t see the whole picture behind the numbers. Contrary to the graph it’s clear that there’s a stock shortage and you need to order more items.
Visual representations provide clarity in decision making reducing the risk of misinterpretation and promoting well-informed choices.
Related Article: How To Make A Bar Graph in Excel?
5 Data Visualization Principles
- Clarity and Simplicity
- Accuracy and Truthfulness
- The Right Visualization Type
- Colors and Visual Appeal
- Avoiding Misleading Visuals
#1 Clarity and Simplicity
- Keep it simple: Avoid clutter and excessive complexity.
- Use clear labels and titles: Make sure viewers understand what they’re looking at.
- Choose appropriate visual elements: Select charts and graphs that best convey your message.
Simplicity is the ultimate sophistication in visualization. An overload of elements can obscure the message. Clean visuals with minimal distractions ensure that the audience’s focus remains on the data story. Keeping in mind basic principles design will be easier for you to make storytelling with data.
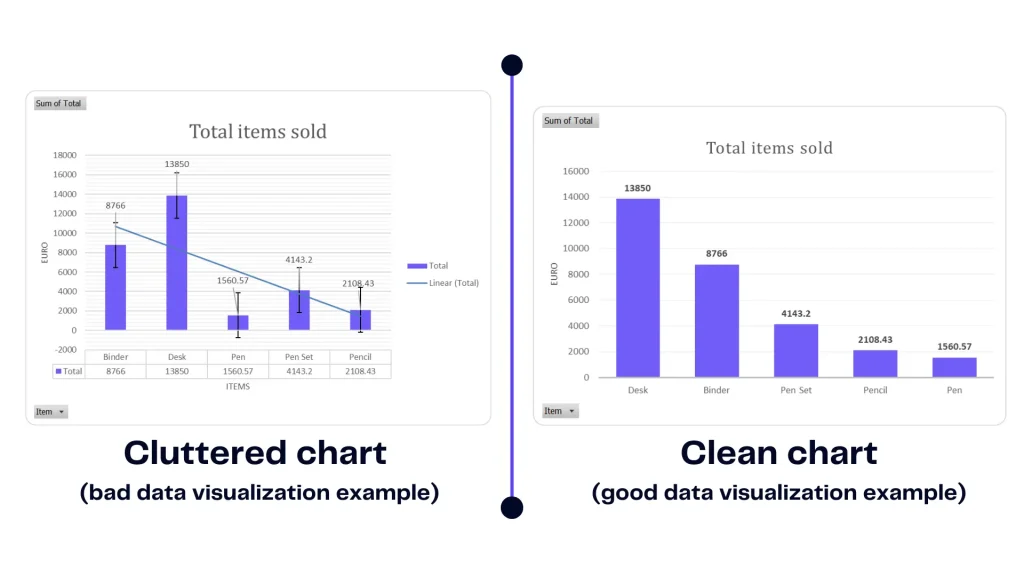
Misleading data visualization examples and good visualization, image by author
An example presents the difference between a cluttered chart and a clean chart. You should aim for the one on the right. The first chart contains too many labels and information that it’s hard to understand. Find out how to visualize financial data.
It’s unclear what is the story behind this chart. However, a clean chart highlights important information therefore it’s easy to make a decision.
Related Article: How To Change Series Name in Excel?
#2 Accuracy and Truthfulness
- Represent data accurately: Ensure that the visuals reflect the data correctly.
- Avoid misleading visuals: Be cautious of techniques that can distort the data.
- Provide context: Offer additional information to help viewers interpret the data.
Before you create visualizations, you should clean and prepare the information. This involves removing inconsistencies, filling gaps, and ensuring accuracy. The adage “garbage in, garbage out” rings true – without clean data, even the most compelling visuals can lead to incorrect conclusions.
#3 Right Visualization Type
The world of visualization is diverse, offering a plethora of chart types: bar charts, pie charts, histograms, and more. Visualizing graph data from the amount of data with radar chart, line graph, and time series analysis.
| Visualization Type | Best At | Less Suitable For |
|---|---|---|
| Pie Chart | – Comparing parts of a whole (percentages) – Showcasing categorical data with limited categories (usually 4 or less) | – Complex data with many categories – Highlighting trends or relationships over time |
| Bar Chart | – Comparing categories of data – Showing trends or changes over time (horizontal bar charts) | – Large datasets with many categories – Visualizing proportions within a category |
| Line Chart | – Showing trends or changes over time – Comparing multiple trends | – Highlighting specific data points – Visualizing complex relationships between variables |
| Column Chart | – Comparing categories of data – Highlighting magnitudes or differences between categories | – Showing trends over time (less effective than line charts) |
| Scatter Plot | – Identifying relationships between two variables – Visualizing outliers or clusters in data | – Comparing more than two variables – Communicating trends to a broad audience |
| Heatmap | – Identifying patterns or trends across multiple categories – Visualizing data with two or more dimensions | – Highlighting specific data points – Datasets with very few categories |
| Map Chart | – Displaying geographical data – Visualizing trends or patterns across geographic locations | – Data without a geographic component – Complex data with many variables |
| Box Plot | – Comparing distributions of data across categories – Identifying outliers in data | – Large datasets with many categories – Visualizing trends over time |
| Stacked Bar Chart | – Showing the composition of a whole across multiple categories – Comparing trends for multiple categories over time | – Datasets with many categories – Highlighting individual data points |
| Area Chart | – Showing the magnitude or change of a value over time (similar to a line chart) – Emphasizing the volume or total quantity under the curve | – Highlighting specific data points – Comparing trends for many datasets simultaneously |
| Treemap | – Visualizing hierarchical data structures – Identifying relationships between parts of a whole | – Data with very deep hierarchies – Datasets with many categories that are not hierarchical |
| Time Series Chart | – Showing trends or changes over time – Highlighting specific periods or events within the time series | – Comparing many trends simultaneously – Data with high frequency |
| Donut Chart | – Similar to pie charts, for comparing parts of a whole (percentages) – Can accommodate slightly more categories than the pie chart due to the open center – Useful for highlighting a specific metric in relation to the whole | – Data with many categories (can become cluttered) – Not ideal for comparing trends over time |
Each has its strengths and weaknesses, and understanding these nuances helps in selecting the right tool for the job. Learn how to create an effective data dashboard that tells a story.
Related Article: How To Delete A Chart in Excel?
#4 Colors and Visual Appeal
- Use a consistent style: Maintain a cohesive visual appearance throughout the visualization.
- Choose appropriate colors: Select colors that are easy to distinguish and visually appealing.
- Consider the overall design: Pay attention to the layout and composition of the visualization.
Colors are more than aesthetics – they convey meaning. Proper color selection can highlight key points, differentiate categories, and evoke emotions, all of which enhance the effectiveness of visualization.
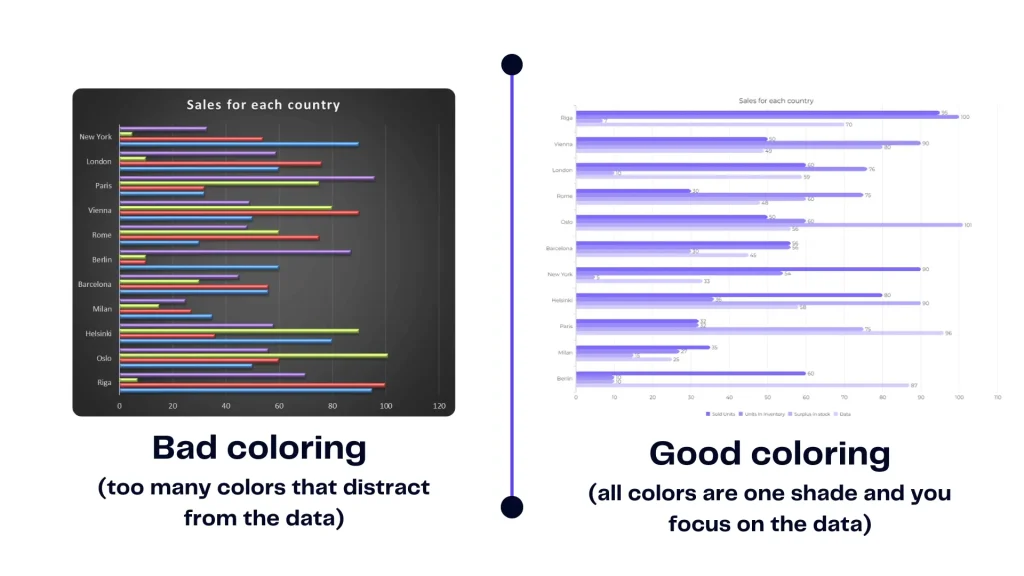
Good vs bad coloring chart example, image by author
Harmony in color palettes isn’t just about aesthetics; it’s about aiding perception. Poorly chosen color combinations can lead to confusion or misinterpretation. Harmonious palettes ensure that the message remains crystal clear. You can use AI that will match and pick the colors for your charts.
Visualizations excel at unearthing hidden relationships. Scatter plots reveal correlations, while line charts expose trends. These patterns might remain invisible in raw info but become evident through the power of visuals. Explore the world of business intelligence and analytics.
See the example above to understand best practices for simple data correlation visualization.
#5 Avoiding Misleading Visuals
- Use appropriate scales and units: Select scales that accurately represent the data.
- Focus on the key message: Ensure that the visualization supports your main point.
- Consider the audience: Tailor the visualization to the needs and understanding of your viewers.
Misleading visuals can lead to misguided conclusions. It’s crucial to be aware of pitfalls like distorted scales, truncated axes, and inappropriate comparisons. Ir will ensure that your visualizations remain accurate.
Ensuring accurate and ethical information representation is key. Integrity is paramount in visualization. Accurate representation involves transparently presenting data points, acknowledging uncertainty, and avoiding manipulative techniques that can distort the truth. Explore good dashboard examples here.
Related Article: How To Explode A Pie Chart in Excel?
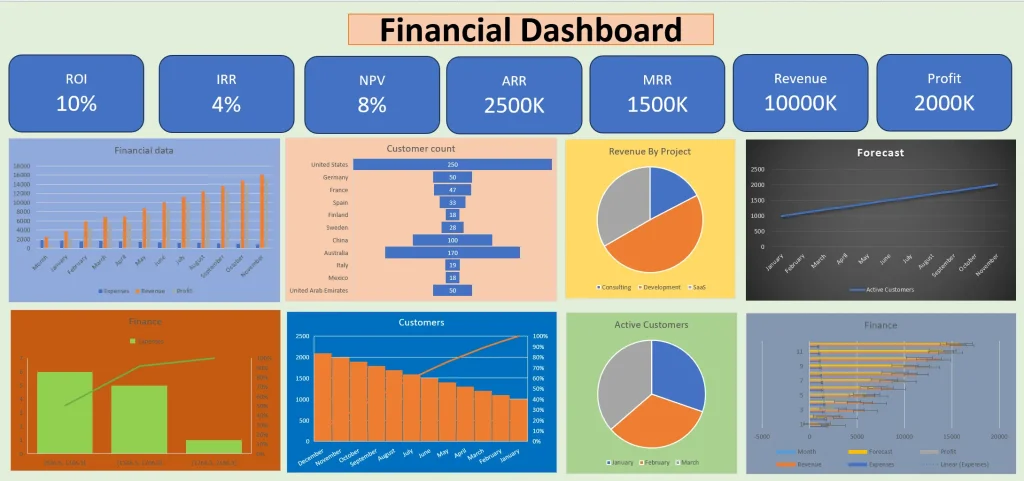
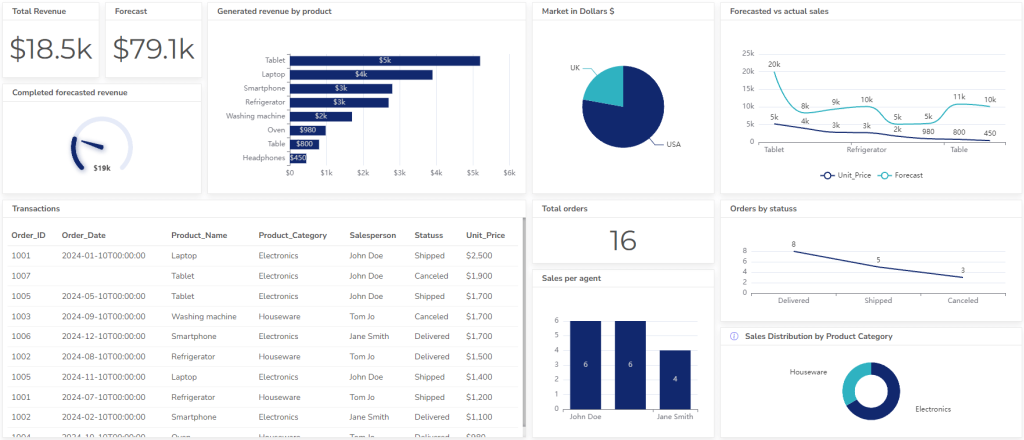
How To Visualize Data With Ajelix BI?
Time needed: 1 hour
Here’s a step-by-step guide on how easy it’s to create professional-looking dashboards using Ajelix BI report builder.
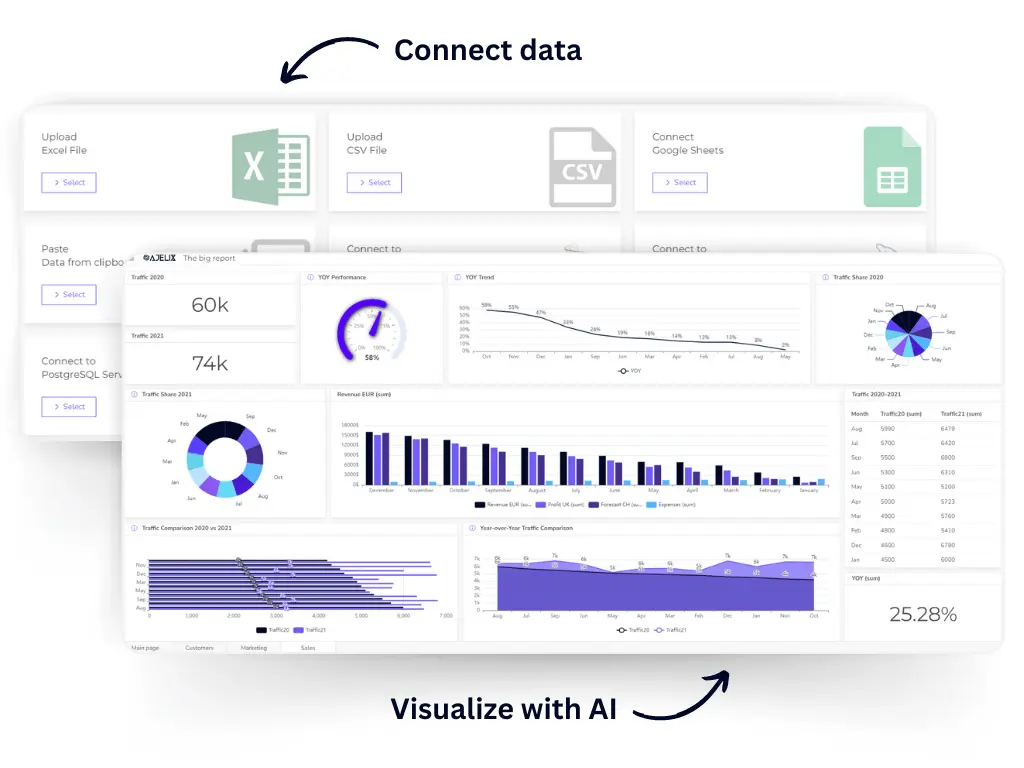
- Data Upload or Connection
Upload: Prepare your data as a CSV, Excel, or Google Sheets. Drag and drop it onto the Ajelix BI platform or use the upload option.
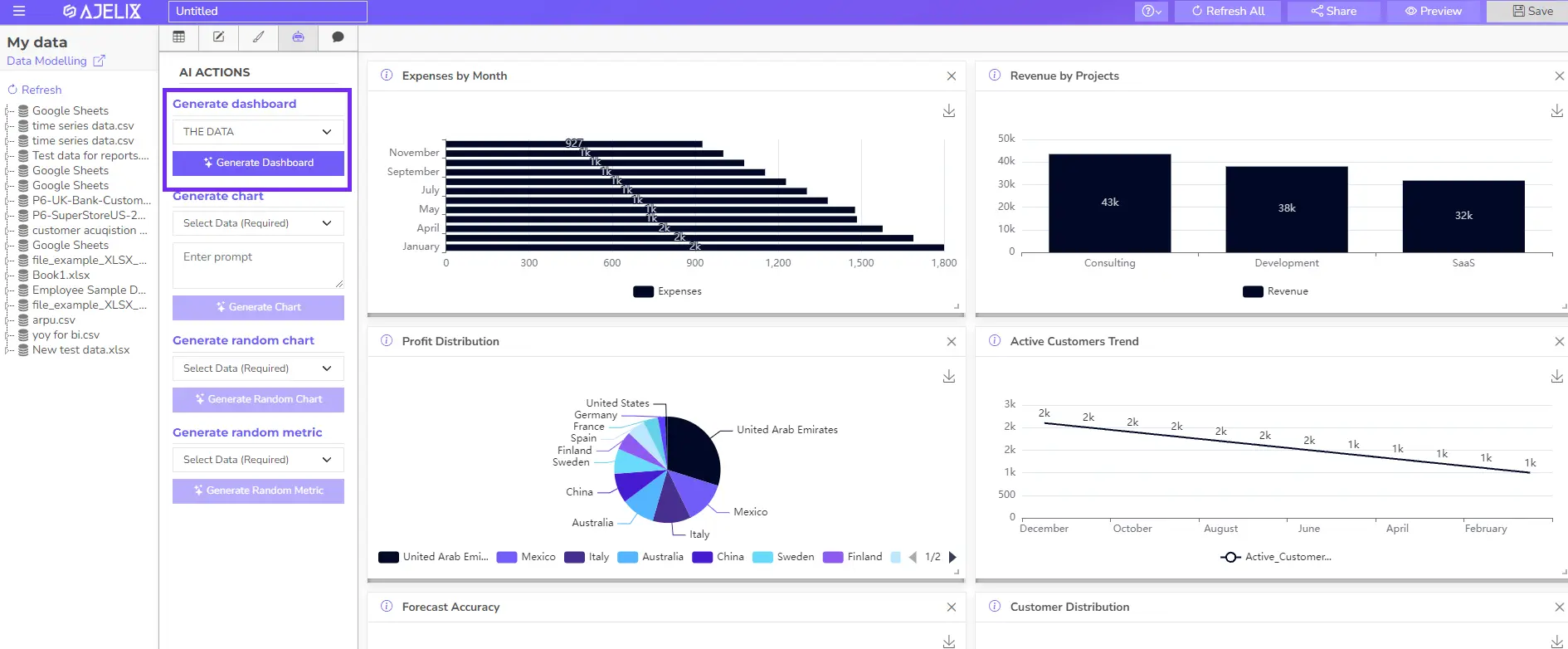
SQL Connection: If your data resides in an SQL server, Ajelix BI offers a direct connection. Provide your server credentials and choose the relevant database/table. - Use AI Dashboard Generator for faster result
For quick and efficient visualization you can use an AI-powered dashboard generator. Select the dataset and AI will analyze your data and suggest a dashboard layout with relevant charts. You can use this as a starting point to customize it further.
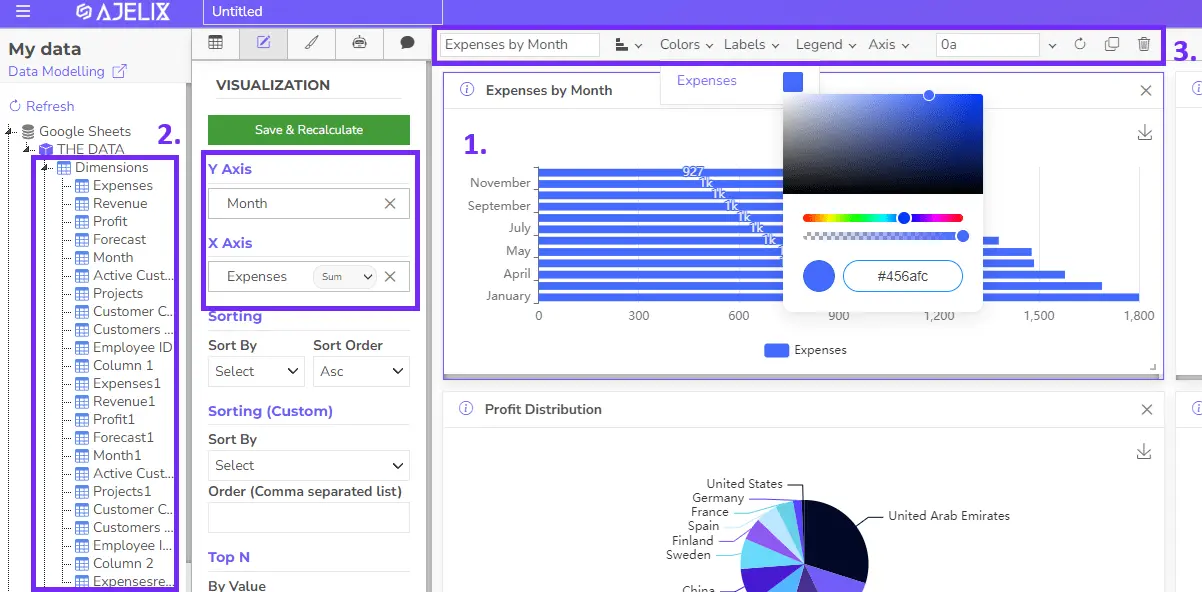
- Customization
1. From the available chart types (bar, line, pie, etc.), drag and drop the desired ones onto your workspace.
2. Assign specific data fields from your uploaded data to each chart for visualization.
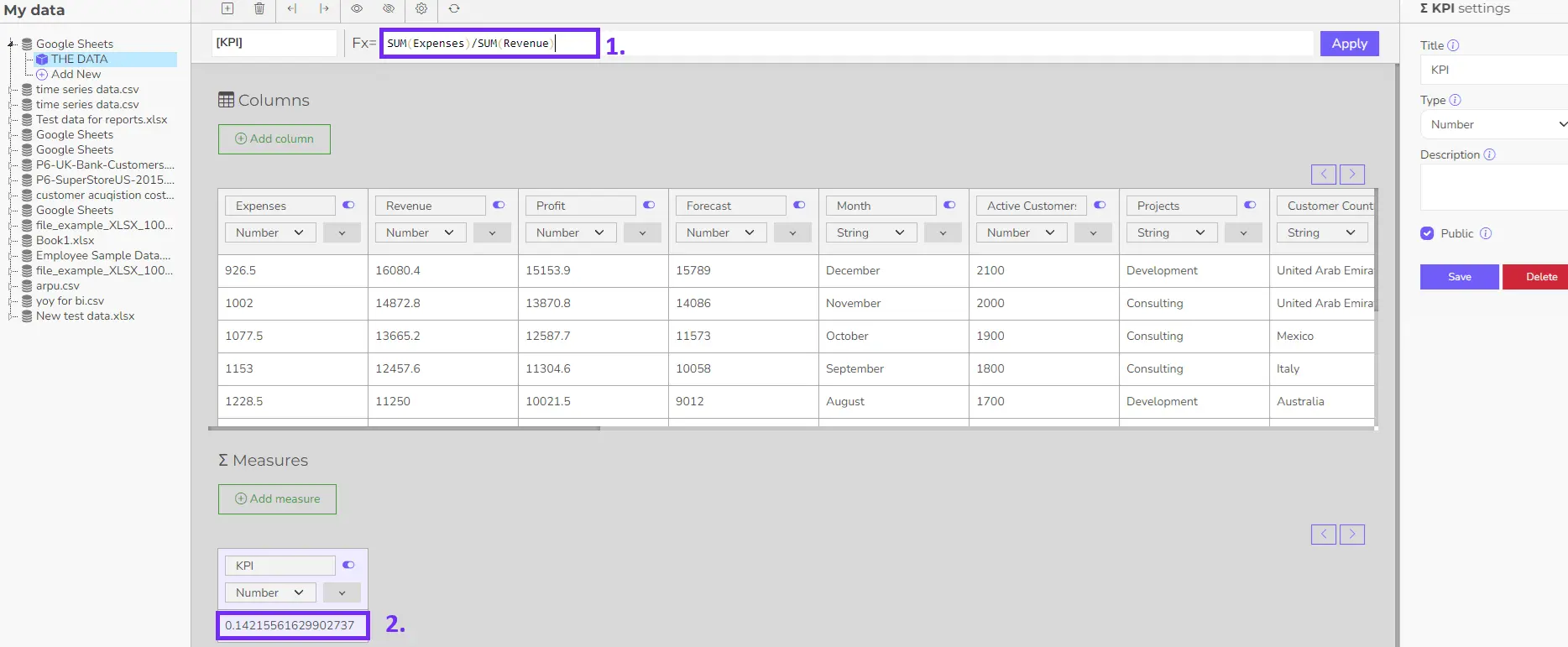
3. Customize chart appearance (colors, fonts, labels) and data formatting (number displays, percentages) using the provided options. - Advanced KPI Creation With SQL Functions (Optional):
For complex KPI creation, Ajelix BI allows the writing of custom SQL queries within the platform. This enables calculations, aggregations, and data manipulation beyond the basic options. To get these features go to “Data modeling”
Note: Experience with SQL is recommended for this step but not mandatory if the user understands Excel formula syntax. - Sharing Your Dashboard
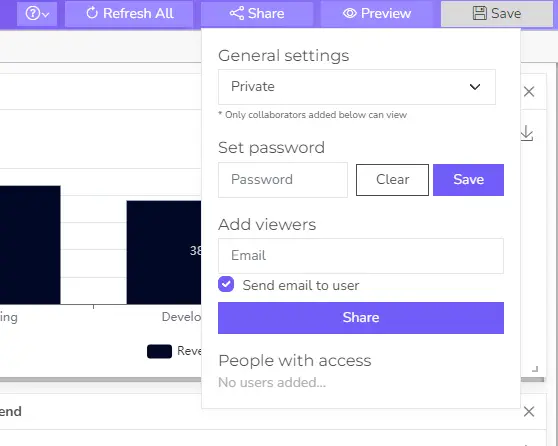
Once satisfied with your visualization, click the “Share” option. Ajelix BI will generate a unique link for your dashboard. Share this link with anyone you want to grant access to view your data visualization.
Additional Tips:
- Ajelix BI offers tutorials and documentation to help you navigate the platform and explore its features in more detail.
By following these steps, you can leverage Ajelix BI to transform your data into clear and insightful visualizations. Remember, start with the basic data upload or connection, then explore customization and advanced options based on your needs.
Ready to give it a go?
Connect your data and create professional reports
Start free
Try free and upgrade whenever
Choosing the Right Tools for the Job
Now that you understand the core principles of data visualization, it’s time to explore the tools that can help you bring your data stories to life. There’s a vast array of data visualization software available, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Selecting the right tool depends on several factors, including:
- Data Complexity: Simple spreadsheets might be manageable with basic tools like Microsoft Excel, while complex datasets might require more sophisticated software like Tableau or Power BI.
- Technical Expertise: Some tools offer drag-and-drop interfaces for beginners, while others require programming knowledge for advanced customization.
- Budget: Free and open-source options exist, but premium software often unlocks additional features and functionalities.
- Collaboration Needs: If teamwork is crucial, consider cloud-based tools that facilitate shared dashboards and real-time updates.
Tools For Easy Data Visualization
- Ajelix BI: user-friendly drag-and-drop self-service platform with AI functionality. Great option for small business owners who need basic analytics features.
- Tableau: Industry leader with powerful features for data manipulation, analysis, and visualization. Offers a wide variety of chart types and customization options.
- Power BI: Microsoft’s business intelligence platform known for its integration with Excel and other Office products. Well-suited for creating interactive dashboards and reports.
- Qlik Sense: User-friendly tool with a focus on self-service analytics and data exploration. Known for its intuitive interface and associative data exploration capabilities.
Did you know..?
Businesses already use AI to create data dashboards with 1-click. Check our latest feature on Ajelix BI platform and uncover AI insights from your data.
Free and Open-Source Tools:
- Google Data Studio: A user-friendly platform for creating interactive dashboards and reports. Integrates seamlessly with other Google products like Sheets and Analytics.
- Tableau Public: Free version of Tableau with limited publishing capabilities. Great for exploring the software and creating basic visualizations.
- Apache Spark: Open-source framework for large-scale data processing and visualization. Ideal for data scientists and developers working with Big Data.
Other Notable Options:
- Infogram: Cloud-based platform ideal for creating social media-friendly infographics and reports.
- Looker: Data exploration and business intelligence platform geared towards developers and data analysts.
- Zoho Analytics: Comprehensive business intelligence suite with data visualization capabilities. Integrates with other Zoho products and services.
Remember, the “best” tool is subjective. Experiment with different options to find one that aligns with your specific needs, skillset, and budget. Most data visualization tools offer free trials, allowing you to test-drive the features before committing.
Conclusion
Good data visualization examples isn’t just about aesthetics – it’s a science that marries data and design to communicate insights. Clean visuals, meaningful narratives, and accurate representation are the cornerstones of effective data visualization.
Learn more about Excel and Google Sheets hacks in other articles. Stay connected with us on social media and receive more daily tips and updates.
FAQ
Bar charts are for comparing categories (e.g., sales by region). However, line charts show trends over time (e.g., stock price over months).
Here are some common data visualization mistakes to avoid, all concise:
Clutter: Too many elements or data points in one chart.
Unclear Labels: Missing or confusing axis labels and chart titles.
Misleading Colors: Colors not intuitive or not accessible to colorblind viewers.
Wrong Chart Type: Using a bar chart for trends (use line chart) or vice versa.
3D Effects: Distracting and can distort data perception.
Here are a few options: Spreadsheets (Excel, Google Sheets), Presentation Software (PowerPoint, Keynote), Standalone Tools (Ajelix BI, Power BI), and Online Tools (Canva, Infogram).
Spruce up your data viz with these quick tips:
Focus on Clarity: Keep it simple and avoid clutter.
Color Counts: Use color strategically to highlight key data points.
Consistent Design: Maintain consistent fonts, colors, and styles throughout.
Label It Right: Clear and concise labels for axes, titles, and data points.
Whitespace is Key: Don’t cram elements – allow breathing room for visual impact.