- Home
- Product
- Tools
- AI Data Analyst
- Excel Formula Generator
- Excel Formula Explainer
- Google Apps Script Generator
- Excel VBA Script Explainer
- AI VBA Code Generator
- Excel VBA Code Optimizer
- Excel VBA Code Debugger
- Google Sheets Formula Generator
- Google Apps Script Explainer
- Google Sheets Formula Explainer
- Google Apps Script Optimizer
- Google Apps Script Debugger
- AI Excel Spreadsheet Generator
- AI Excel Assistant
- AI Graph Generator
- Pricing
Excel AVERAGE Formula
Complete Guide + Examples
2 min read
Beginner
Free template
TL;DR
Use
=AVERAGE(range)
to calculate the mean of values. For conditional averages, use
AVERAGEIF
or
AVERAGEIFS
. describe what you need below and let AI write it for you.
Formula Generator
=AVERAGE(A1:A10,C1:C10)
=AVERAGE(A1:A100)
=AVERAGE(A1:A10,C1:C10)
=AVERAGEIF(A:A,"May",B:B)
AVERAGE calculates the arithmetic mean of all numeric values in the entire column A. The colon notation (A:A) references all cells in the column.
AVERAGE calculates the mean of all values from cell A1 to A100, summing them and dividing by the count of numeric cells.
AVERAGE calculates the mean across two separate ranges: A1 through A10 and C1 through C10, treating all values as one dataset.
AVERAGEIF calculates the average of values in column B only where the corresponding cell in column A contains “May”.
Pro Tip
1What is the AVERAGE Formula in Excel?
The AVERAGE function in Excel calculates the arithmetic mean of a set of values. It takes the sum of all values and divides it by the count of numeric values in the range. It’s one of the most fundamental statistical functions in spreadsheets.
Common use cases:
-
Calculate average sales performance
-
Determine average monthly expenses
-
Find mean test scores
-
Compute average response times
2AVERAGE Syntax
=AVERAGE(number1, [number2], …) | Argument | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
number1 | Yes | The first number, cell reference, or range to average
|
number2 | Optional | Additional numbers, cell references, or ranges (up to 255 arguments) |
3How to Calculate Average in Excel
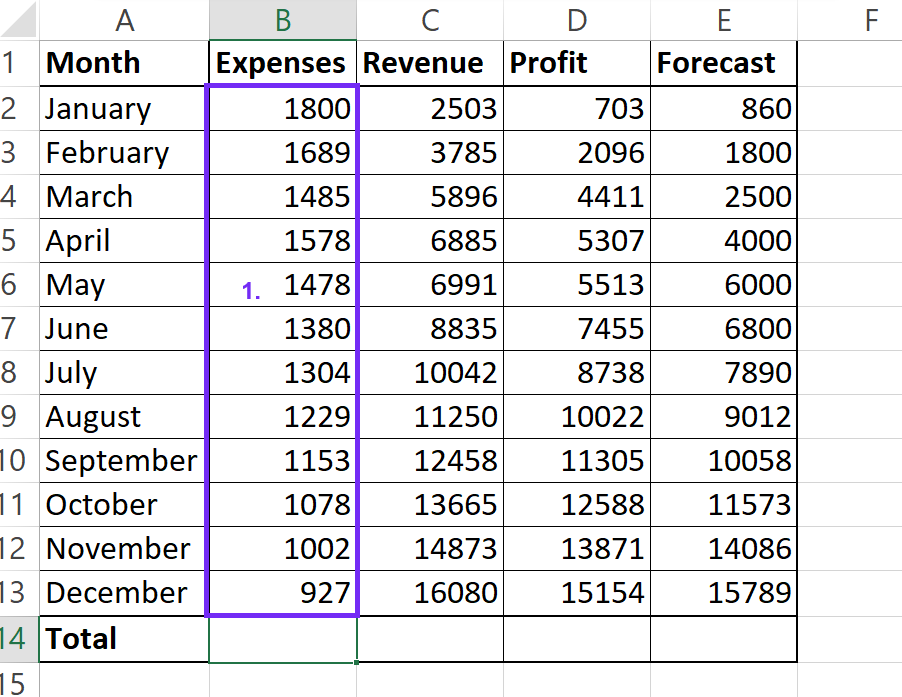
1Identify Your Data
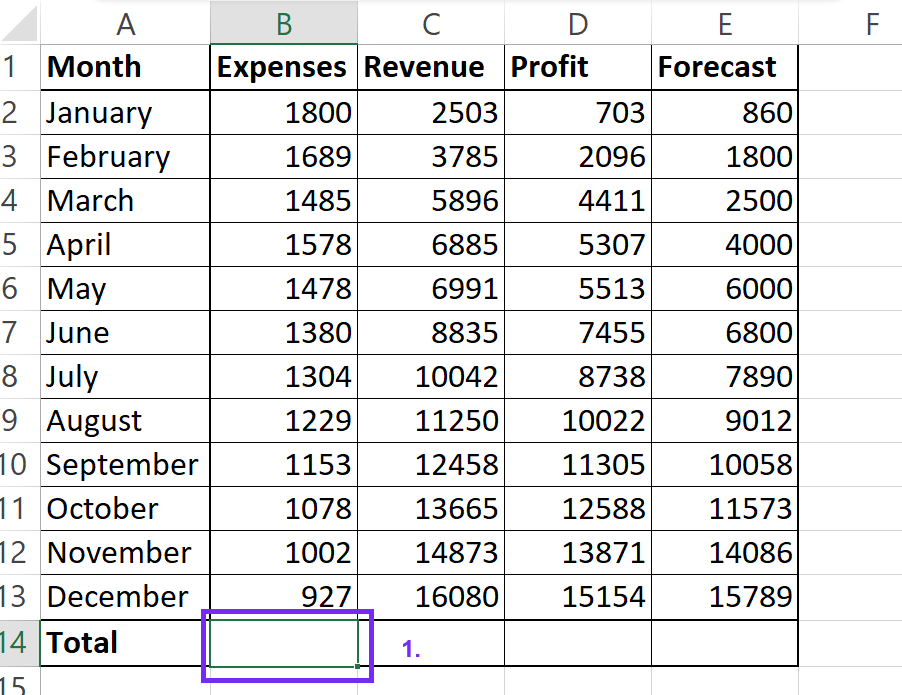
2Select the Output Cell
3Enter the Formula
=AVERAGE( and Excel will start suggesting functions.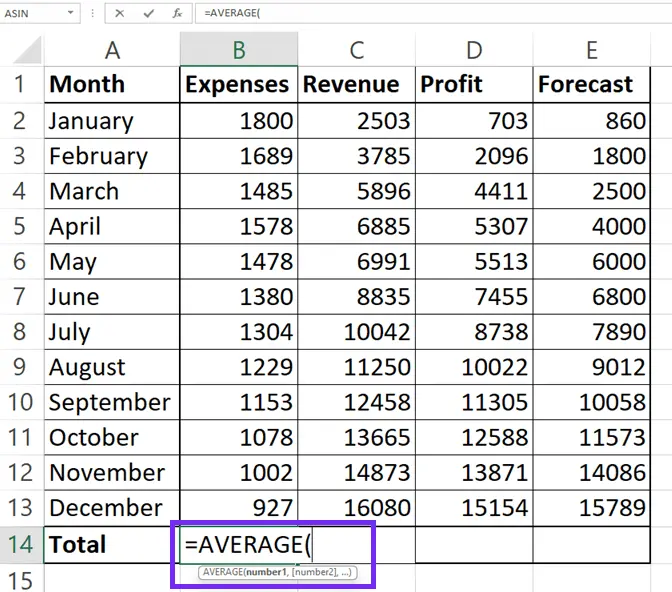
4Select the Range
A1:A10).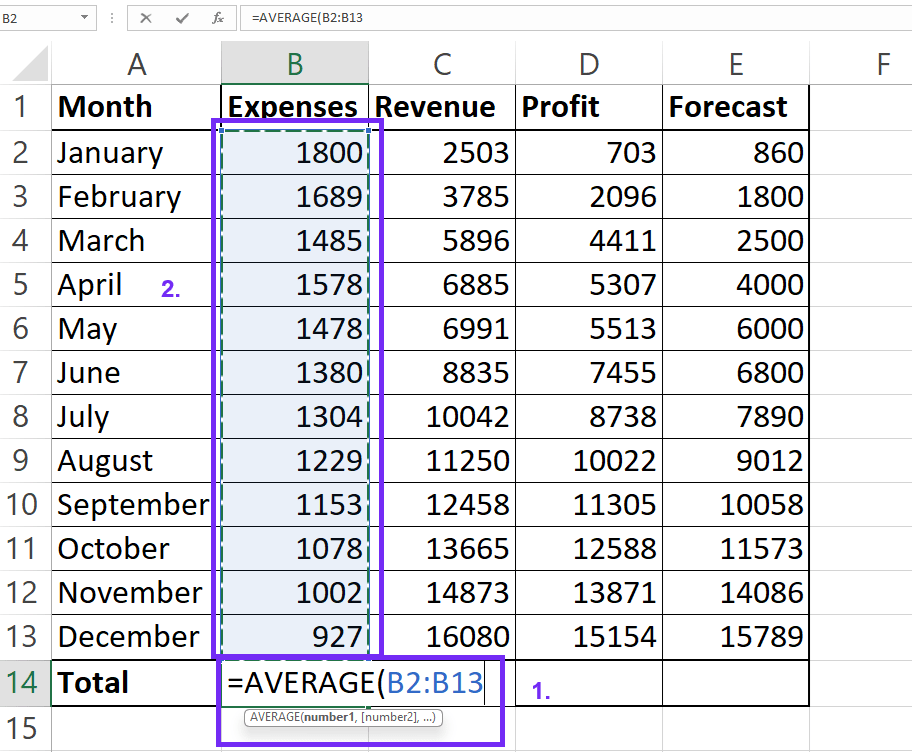
5Close & Execute
) to close the parenthesis and press Enter.
Skip the manual work
4Calculating Averages Across Multiple Ranges
=AVERAGE(A1:A10, C1:C10, E1:E10) For non-adjacent cells in the same row, you can also use:
=AVERAGE(A1, C1, E1) 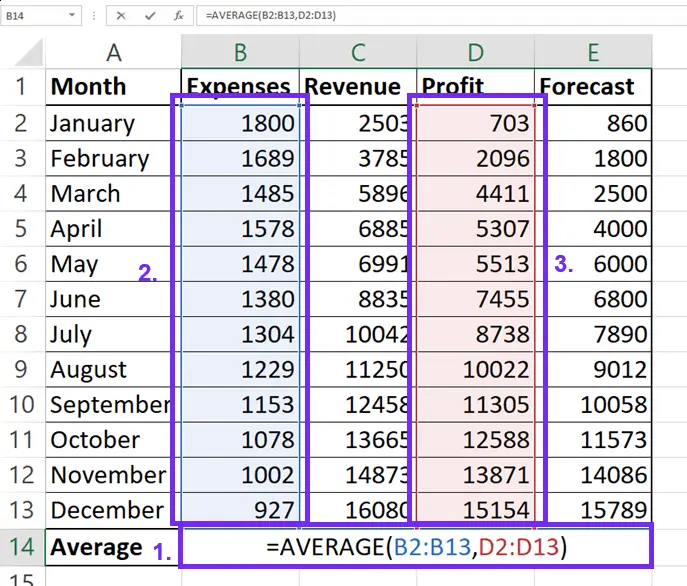
Multiple Ranges
5Averaging an Entire Column
=AVERAGE(A:A) 
Dynamic Updates
6AVERAGEIF Function (Single Criterion)
=AVERAGE(range, [criteria], [average_range]) Example: To average values in column B where column A contains “May”:
=AVERAGEIF(A:A, "May", B:B) 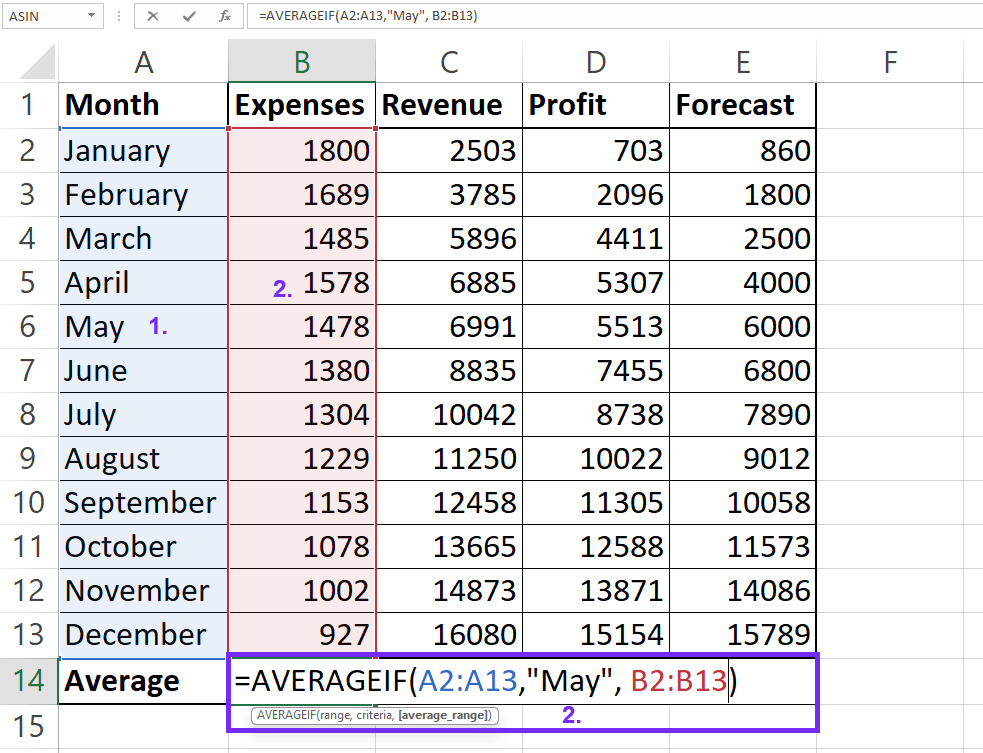
| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
range | The range of cells to evaluate against the criteria
|
criteria | The condition that must be met (e.g., “May”, “>100”)
|
average_range | The actual cells to average (optional if same as range)
|
7AVERAGEIFS Formula(Multiple Criteria)
=AVERAGEIFS(average_range, criteria_range1, criteria1, ...)
Example: To average values in column C where column A is “May” AND column B is “Project B”:
=AVERAGEIFS(C:C, A:A, "May", B:B, "Project B") 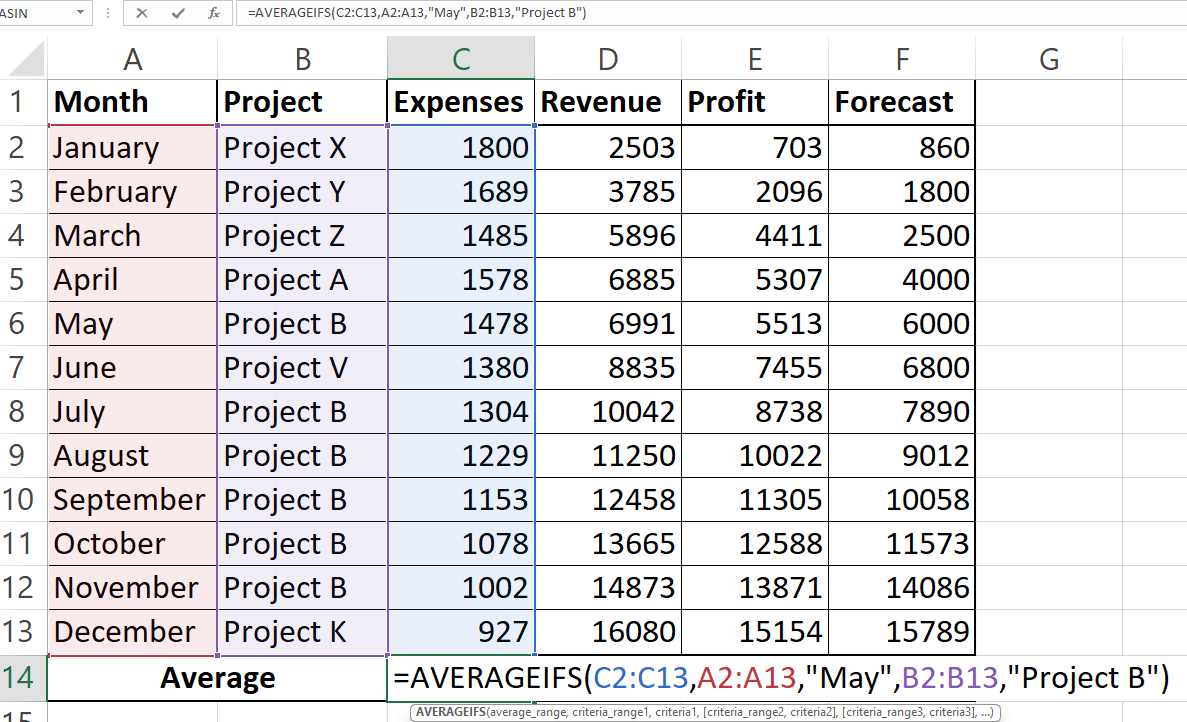
Note the Difference
8Quick Average Using the Status Bar
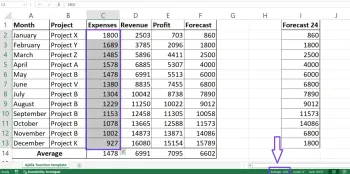
1Select your data
2Check the Status Bar
Download Free Excel Template
Download Free Excel Template
?Frequently Asked Questions
Use the AVERAGE function and list each range separated by commas within the parentheses. For example: =AVERAGE(A1:A10, C1:C10, E1:E10). This is how to find average in Excel with scattered data.
You can use the AVERAGE function by specifying the ranges of your columns. For example, =AVERAGE(A:A, C:C, E:E) will average entire columns A, C, and E.
Use AVERAGEIF for one criterion or AVERAGEIFS for multiple criteria. For example: =AVERAGEIF(A:A,"North",B:B) averages column B where column A equals “North”.
No, the AVERAGE function ignores empty cells and text values. It only calculates the mean of numeric values in the specified range.
AVERAGE ignores text and logical values, while AVERAGEA includes them (treating text as 0, TRUE as 1, and FALSE as 0). Use AVERAGEA when you need to include all cell types in your calculation.