- Home
- Data Visualization
- Tools
- Excel Formula Generator
- Excel Formula Explainer
- Google Apps Script Generator
- Excel VBA Script Explainer
- Excel VBA Script Generator
- Excel VBA Code Optimizer
- Excel VBA Code Debugger
- Google Sheets Formula Generator
- Google Apps Script Explainer
- Google Sheets Formula Explainer
- Google Apps Script Optimizer
- Google Apps Script Debugger
- Excel File Translator
- Excel Template Generator
- Excel Add-in
- Your Virtual AI Assistant For Excel Spreadsheets
- AI Answer Generator
- AI Math Solver
- AI Graph Generator
- Pricing
- Resources
What is Data Visualization? Examples & Definition
-
Author:Agnese
-
Published on:October 17, 2023
-
Category:
-
Last updated:June 21, 2024
-
Tags:
Data visualization is a powerful tool that transforms complex data into comprehensible visual representations. It’s akin to turning raw data into a captivating story, one that transcends numbers and statistics, allowing us to uncover insights, patterns, and trends that might otherwise remain hidden.
This article will delve into the world of data visualization, explaining what it is, how it works, and showcasing some real-world examples that will make you see your data in a whole new light.
Before you jump in...
Looking to create reporting system fast & painlessly? Check our latest Ajelix BI platform for easy data analytics to help you make data driven decisions.
What is Data Visualization?
Data visualization is the graphical representation of data. It utilizes charts, graphs, and other visual elements to convey information. The goal is to make data more accessible, making it easier for individuals to grasp and work with. Learn more about data visualization principles and best practices.
The Role of Data in Decision-Making
Data is the backbone of decision-making. Businesses, governments, and individuals rely on data to make informed choices. Data visualization empowers stakeholders to make these decisions faster and with greater confidence.
What Are the Benefits of Data Visualization?
The significance of data visualization is undeniable. It’s not just about making data look pretty; it’s about making it meaningful. By visually representing data, we gain a deeper understanding of it.
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Simplifies Complexity | Transforms raw data into clear visuals for easier understanding. |
| Reveals Patterns & Trends | Helps identify hidden trends, correlations, and outliers in data. |
| Enhanced Decision-Making | Supports faster and more confident decisions with clear data visualization. |
| Improved Communication & Engagement | Makes data more engaging and memorable, fostering better communication. |
| Increased Accessibility | Allows people from all backgrounds to understand and interact with data. |
Importance of data visualization
Data visualization is crucial because it bridges the gap between raw data and human understanding. Here’s why it’s so important:
Enhanced Data Comprehension
Data visualization is a critical tool for transforming raw data into clear insights. It facilitates the identification of patterns, trends, and relationships within complex datasets, akin to illuminating hidden structures within a vast archive. This improved understanding empowers researchers and analysts to unlock the full potential of their data.
Data-Driven Decision Making
Data visualization transcends mere information presentation; it fosters evidence-based decision making. By translating complex data sets into clear and concise visuals, it empowers stakeholders to make informed choices. Visualizations allow for the efficient comparison of options, highlighting strengths, weaknesses, and potential areas for improvement.
Effective Communication
Data visualization bridges the communication gap inherent in purely technical data analysis. It translates intricate concepts and statistical jargon into a universally understood visual language. Charts, graphs, and maps become powerful tools for conveying complex information to a broader audience, fostering collaboration and knowledge sharing across disciplines.
Communicating Complex Information
One of the most significant advantages of data visualization is its ability to simplify complex information. Whether it’s a convoluted financial report or intricate scientific findings, visualizations provide clarity that words alone cannot convey.
Enhancing Data Understanding
Visualizations engage our visual and cognitive senses simultaneously, facilitating a quicker and more profound understanding of data. They break down barriers between data and comprehension, making the invisible patterns visible.
Types of Data Visualization
Bar charts, line charts, pie charts, and scatter plots – each has a specific purpose and is suitable for different types of data. Exploring these types is the first step in mastering data visualization.
Bar Charts and Column Charts
Bar and column charts are excellent for comparing different categories of data, such as sales figures by region or products.
Line Charts and Area Charts
Line and area charts are perfect for tracking trends over time, whether it’s stock prices or temperature fluctuations.
Pie Charts and Donut Charts
Pie charts offer a visual representation of parts within a whole, making them ideal for showing market share or budget allocation.
Scatter Plots and Bubble Charts
Scatter plots and bubble charts reveal relationships between variables, helping identify correlations and outliers.
Heatmaps
Heatmaps are exceptional for visualizing density and patterns, often used in fields like epidemiology and user behavior analysis.
Sankey Diagrams
Sankey diagrams display flow and quantity relationships, making them indispensable for visualizing processes and resource allocation.
Treemaps
Treemaps are excellent for hierarchical data, showing the relationships between entities and sub-entities.
Radar Charts
Radar charts, also known as spider or web charts, help compare multiple variables across a common axis.
Data Visualization Tools
A broad spectrum of data visualization tools is available, ranging from free, open-source options to powerful commercial software.
Open-Source vs. Commercial Tools
Deciding between open-source and commercial tools depends on factors like budget, customization needs, and the complexity of your projects.
Popular Data Visualization Software
Software like Ajelix BI, Tableau, Power BI, and D3.js are at the forefront of the data visualization landscape, each offering unique features and capabilities.
Creating Data Visualizations with Excel
Even a widely-used tool like Microsoft Excel can create compelling data visualizations, offering a cost-effective solution for many users.
Excel’s Charting Capabilities
Excel’s charting capabilities allow you to create various visualizations, including bar charts, line graphs, and more.
Limitations and Alternatives
While Excel is versatile, it has limitations in handling large datasets and complex visualizations. Alternative software like R and Python libraries offer more advanced options.
Best Practices in Data Visualization
Effective data visualization adheres to principles like simplicity, clarity, and meaningful use of color.
The Importance of Simplicity
Simplicity is key. Extraneous details can distract from the core message, so it’s crucial to simplify visualizations to their essence.
Choosing the Right Chart Type
Selecting the right chart type is an art. It depends on the data and the story you want to convey.
Storytelling through Data Visualization
Data visualization is not just about presenting numbers. It’s about telling a story with data.
Crafting a Narrative with Data
Crafting a narrative engages the audience emotionally, ensuring that data is not just understood but remembered.
Incorporating Context and Insights
Adding context and insights to data visualizations makes them more informative. It helps the audience understand the “why” behind the data.
Data Visualization Examples
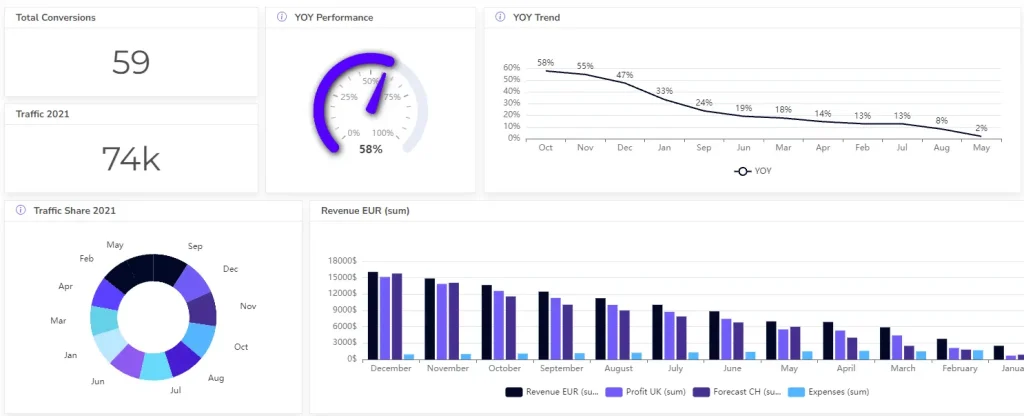
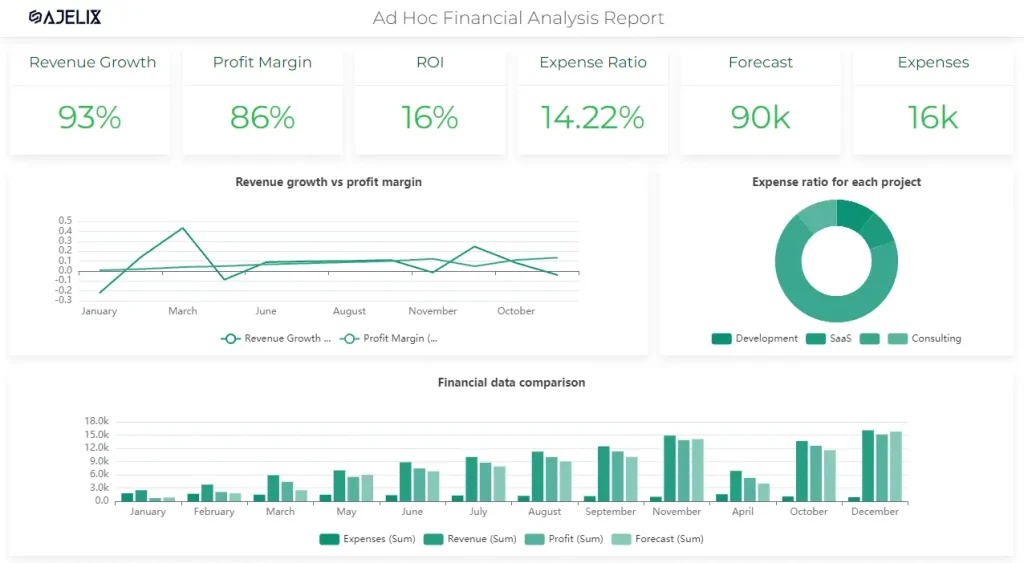
Sales and Revenue Visualizations
Visualizing sales and revenue data can help identify trends and areas for improvement. Examples include sales growth over time and revenue by product category.
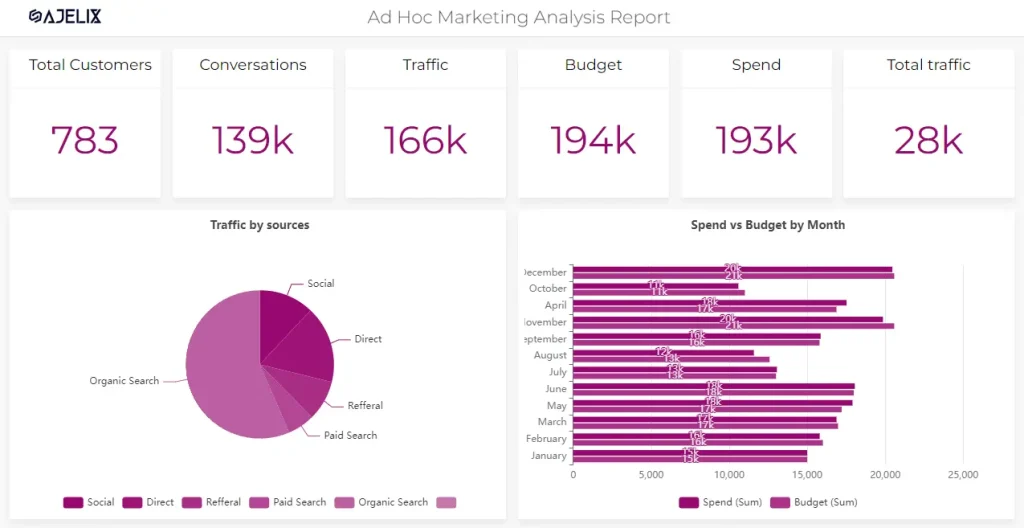
Marketing and Campaign Data Visualizations
Marketing campaigns generate vast amounts of data. Visualizing this data can help assess the effectiveness of strategies, such as social media engagement and email marketing performance.
Health and Medical Data Visualizations
In healthcare, data visualization is used for tracking disease trends and projections, as well as displaying clinical trial outcomes.
Conclusion
The Enduring Relevance of Data Visualization
As the volume of data continues to grow, data visualization remains a cornerstone for unlocking the potential within that data. It transcends industries and domains, empowering professionals to harness insights and drive informed decisions.
Empowering Data-Driven Decision-Making
In an age where data is omnipresent, the ability to visualize and understand it is a superpower. Data visualization is the key to unleashing that power, making it an essential skill for anyone navigating the modern world.
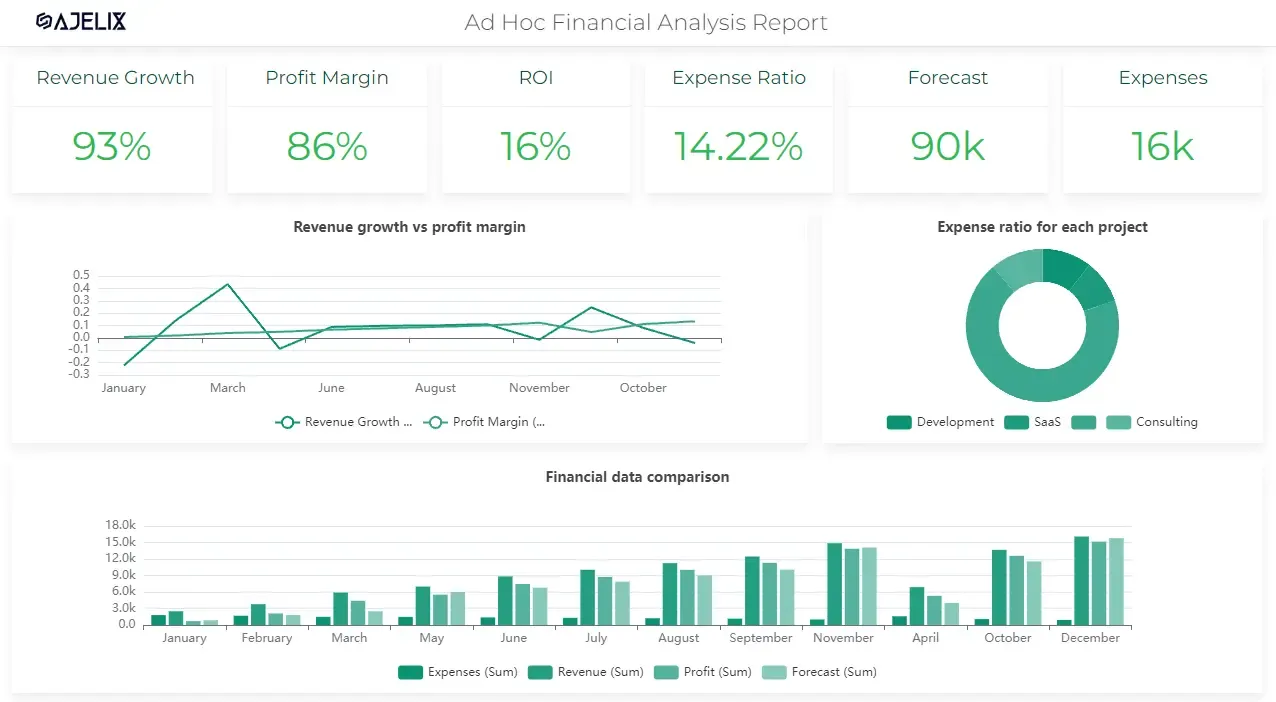
From data to report in one minute or less with Ajelix BI
Similar posts
Data Visualization For Small Business: Where To Start?
Time Series Charts: How To Create & When To Use With Examples
Pie Charts: When To Avoid & How To Use Them With Examples
Business Intelligence & Analytics

20 Financial KPIs For The Finance Department

15 Ecommerce KPIs Any Online Business Should Track

15 Accounting KPIs For Your Accounting Department
Calculators

Free EBIT Calculator Online With Formula Examples

Free Business Loan Calculator Online: Calculate Loan