- Home
- Product
- Tools
- AI Data Analyst
- Excel Formula Generator
- Excel Formula Explainer
- Google Apps Script Generator
- Excel VBA Script Explainer
- AI VBA Code Generator
- Excel VBA Code Optimizer
- Excel VBA Code Debugger
- Google Sheets Formula Generator
- Google Apps Script Explainer
- Google Sheets Formula Explainer
- Google Apps Script Optimizer
- Google Apps Script Debugger
- AI Excel Spreadsheet Generator
- AI Excel Assistant
- AI Graph Generator
- Pricing
-
Author:
Excel Hacks: How To Copy Conditional Formatting
-
Last updated:January 11, 2025
-
Tags:

Explore other articles
- What AI Studies Say About Agentic AI ROI & Stats (And What They Don’t)
- Google Sheets AI Agents That Autonomously Perform Tasks
- Advanced Agentic Research With AI Agents
- GLM-5 is Now Available on Ajelix AI Chat
- AI Spreadsheet Generator: Excel Templates With AI Agents
- Excel Financial Modeling With AI Agents (No Formulas Need!)
- AI Landing Page Generator: From 0 To Stunning Page With Agent
- Creating Charts In Excel with Agentic AI – It Does Everything!
- Create Report From Google Sheets Data with Agentic AI
- How To Create Powerpoint Presentation Using AI Agent (+Video)
Try AI in Excel
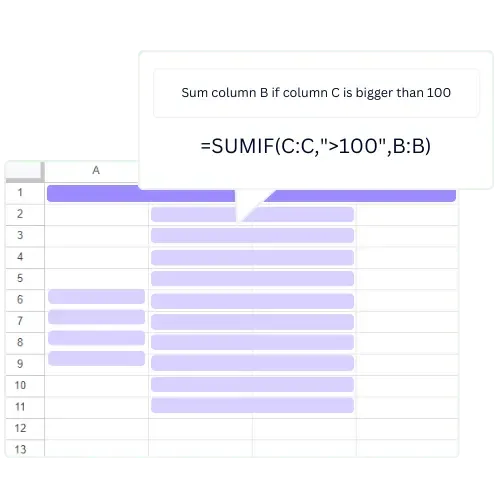
Conditional formatting is a feature in Excel that allows you to format cells based on specific criteria. This can help you to visually organize and highlight important data. This post covers the advantages of conditional formatting and guides you on copying and removing it in Excel.
What Are The Benefits of Conditional Formatting?
Conditional formatting can improve data visualization by making it easier to identify trends and patterns in data sets. It also saves time by automating the formatting process and can help to prevent errors in data entry.
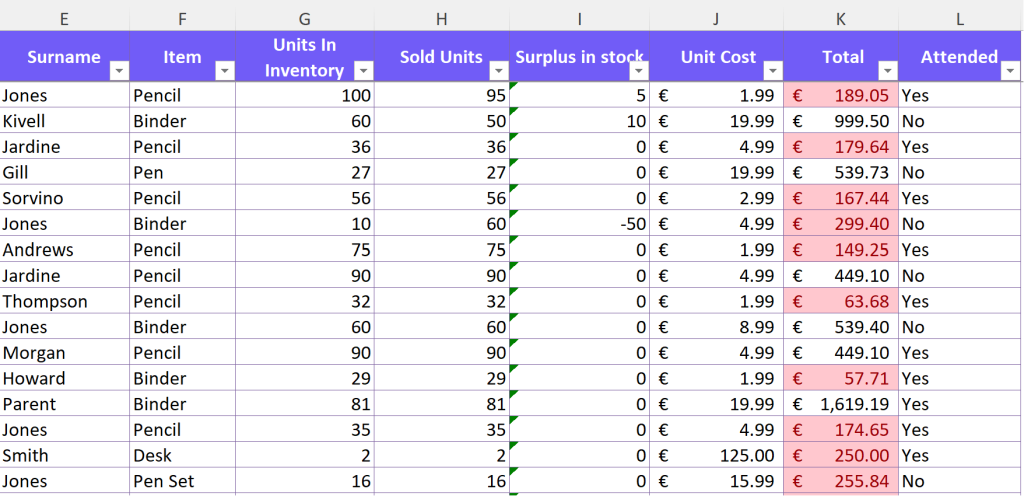
Additionally, it can make your spreadsheets more visually appealing and professional-looking.
How to Copy Conditional Formatting in Excel
Copying conditional formatting can save time, especially for large datasets with uniform formatting.
Conditional formatting is like the Picasso of Excel, adding flair to your data presentation. But what if you want to sprinkle that magic across other cells without redoing the masterpiece? Enter, the art of copying conditional formatting.
Time needed: 2 minutes
Here’s how to copy conditional formatting
- Select the Source
First, highlight the cell with the formatting you want to replicate. This is your source.
- Copy the Format
Right-click on the source cell, choose “Format Painter” from the menu, and watch your cursor transform into a paintbrush.
- Apply to Target
Click on the cell or range where you want the formatting to appear. Voila! The copied formatting is now applied.
- Double-Click for Multi-Use
Want to apply the same formatting multiple times? Double-click the Format Painter, and it stays active until you press “Esc.”
- Clear Formatting
To remove formatting, select the cell and go to “Home” > “Clear” > “Clear Formats.”
Copying conditional formatting in Excel is like cloning style with a few clicks. It’s the shortcut that keeps your spreadsheets aesthetically consistent and your data presentation top-notch.
Related Articles: How to make bar charts bar wider in Excel?
How to Remove Conditional Formatting in Excel
Sometimes you may need to remove conditional formatting from a cell or range of cells. This could be because you no longer need the formatting or because it was applied incorrectly. Next, we’ll show you how to remove conditional formatting in Microsoft Excel, step by step, with useful tips for faster removal. We will also explain the benefits of removing conditional formatting. Learn more in detailed in our article how to remove conditional formatting.
Advanced Conditional Formatting Techniques
We will explore more advanced conditional formatting techniques, such as how to apply conditional formatting to a large range of cells. How to use formulas in conditional formatting, and how to use data bars, color scales, and icon sets in conditional formatting.
Related Article: How to copy formula down?
Troubleshooting Conditional Formatting Issues
Conditional formatting can sometimes create unexpected results or errors. Here are some common issues that may arise, along with tips on how to fix them.
1. Formatting is not being applied correctly
If your formatting is not being applied correctly, check that the range of cells you are applying it to is correct. Make sure there are no empty cells or cells with conflicting formatting within the range.
2. Formatting is being applied to the wrong cells
If formatting is being applied to the wrong cells, check that the correct cells are selected before applying formatting. You can also try clearing any existing formatting before applying the new format style.
3. Formatting is not being applied consistently
If your formatting is not being applied consistently, check that your formulas and rules are correct. You may need to adjust your rules to ensure that they are being applied correctly.
4. Conditional formatting is not updating automatically
By default, conditional formatting will not update automatically if changes are made to the cells. You can manually update the formatting by selecting the cells and pressing F9. Or you can enable automatic updating by going to the “Formulas” tab and clicking “Calculation Options” and then “Automatic”.
Related Article: Excel doesn’t save formatting
Examples of Creative Uses of Conditional Formatting
Conditional formatting can be used in many creative ways to enhance visualizing data and make data easier to read and understand. Here are some innovative examples of conditional formatting.
1. Heat Maps
Heat maps use color scales to visually represent data. For example, a heat map can be used to show which cells have the highest or lowest values in a range.
2. Traffic Light Indicators
Traffic light indicators use icon sets to represent different levels of data. For example, green could indicate good, yellow could indicate fair, and red could indicate poor.
3. Highlighting Duplicates
Conditional formatting can be used to highlight duplicate values in a range, making it easier to identify and remove duplicates.
Other Articles: Excel Dashboard 101: How to Create Effective Dashboards
Best Practices for Using Conditional Formatting
1. Keep it simple
Avoid using too many formatting rules or styles, as this can make data harder to read and understand. Stick to a few key styles or colors that are easy to interpret.
2. Be consistent
Use the same formatting rules and styles throughout your workbook to ensure consistency and make data analysis easier to compare.
3. Use it sparingly
Conditional formatting should be used to enhance data visualization, not to overwhelm it. Use it sparingly and only when it adds value.
4. Document your rules
Make sure to save your formatting rules and styles for future use or sharing with others.
Struggling with your Excel formulas?
Looking for a faster and easier way to write Excel formulas? Try AI Excel Formula Generator and turn your text into formulas with just a few clicks.
Conclusion
Conditional formatting is a powerful tool in Excel that can help you to organize and use data visualization tools effectively. By using the techniques outlined in this blog post, you can save time, prevent errors, and create more professional spreadsheets. We hope that this article has been helpful in explaining how to copy and remove conditional formatting in Excel.
Remember to always test your formatting and be mindful of accessibility. With these Excel hacks in your toolbox, you’ll be able to take your data visualization skills to the next level.
Learn more about Excel and Google Sheets hacks in other articles. Stay connected with us on social media and receive more daily tips and updates.
Frequently Asked Questions
To apply data bars in conditional formatting, select the cell or range of cells you want to format, click the “Conditional Formatting” button in the “Home” tab, select “Data Bars,” and then select the color and style of the data bars.
To apply color scales in conditional formatting, select the cell or range of cells you want to format, click the “Conditional Formatting” button in the “Home” tab, select “Color Scales,” and then select the color scale you want to use.
Yes, you can copy conditional formatting between workbooks in Excel by selecting the cell or range of cells with the formatting you want to copy, clicking the “Format Painter” button in the “Home” tab, selecting the first cell or range of cells in the other workbook, and then double-clicking the “Format Painter” button to apply the formatting to the entire range.
Speed up your spreadsheet tasks with Ajelix AI in Excel