- Home
- Product
- Tools
- AI Data Analyst
- Excel Formula Generator
- Excel Formula Explainer
- Google Apps Script Generator
- Excel VBA Script Explainer
- AI VBA Code Generator
- Excel VBA Code Optimizer
- Excel VBA Code Debugger
- Google Sheets Formula Generator
- Google Apps Script Explainer
- Google Sheets Formula Explainer
- Google Apps Script Optimizer
- Google Apps Script Debugger
- AI Excel Spreadsheet Generator
- AI Excel Assistant
- AI Graph Generator
- Pricing
- Home
- Blog
- Calculators
- Free Debt To Asset Ratio Calculator Online
Free Debt To Asset Ratio Calculator Online

Explore other articles
- Google Sheets AI Agents That Autonomously Perform Tasks
- Advanced Agentic Research With AI Agents
- GLM-5 is Now Available on Ajelix AI Chat
- AI Spreadsheet Generator: Excel Templates With AI Agents
- Excel Financial Modeling With AI Agents (No Formulas Need!)
- AI Landing Page Generator: From 0 To Stunning Page With Agent
- Creating Charts In Excel with Agentic AI – It Does Everything!
- Create Report From Google Sheets Data with Agentic AI
- How To Create Powerpoint Presentation Using AI Agent (+Video)
- Ajelix Launches Agentic AI Chat That Executes Business Workflows, Not Just Conversation
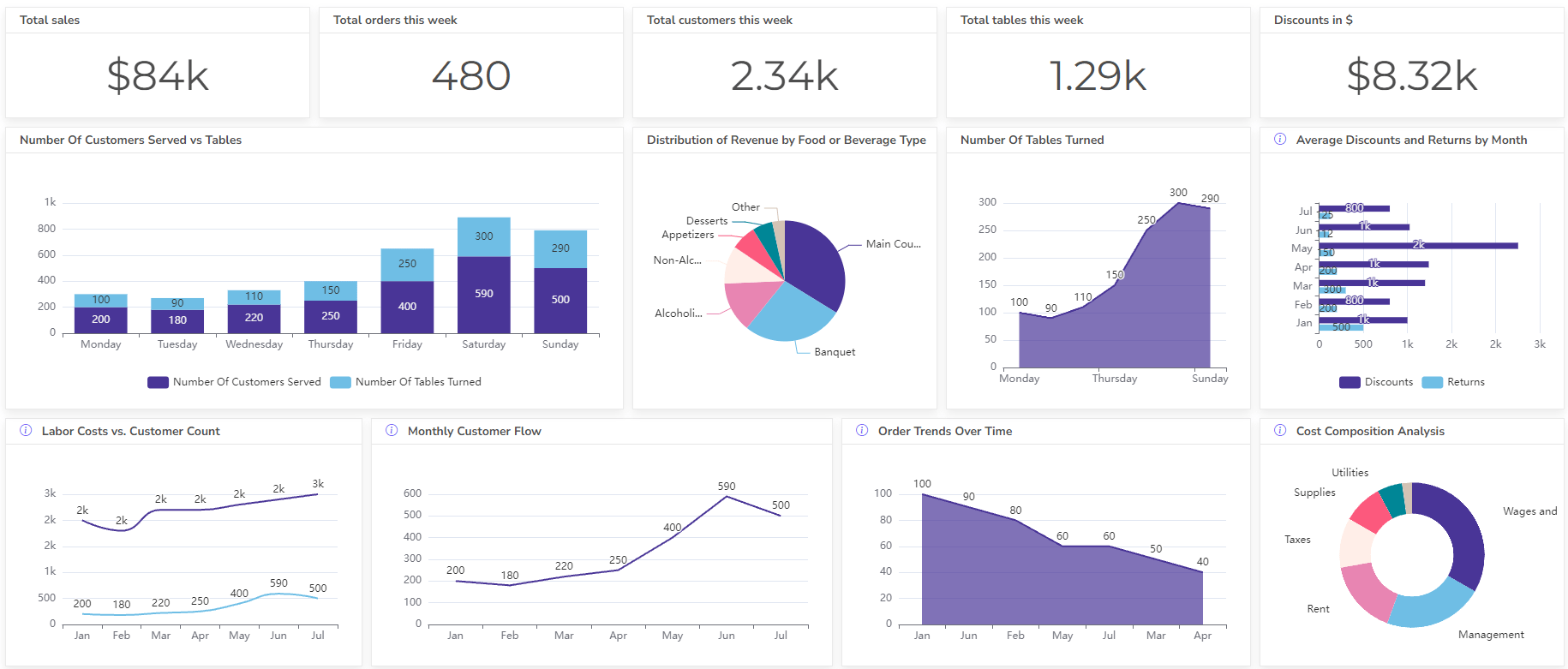
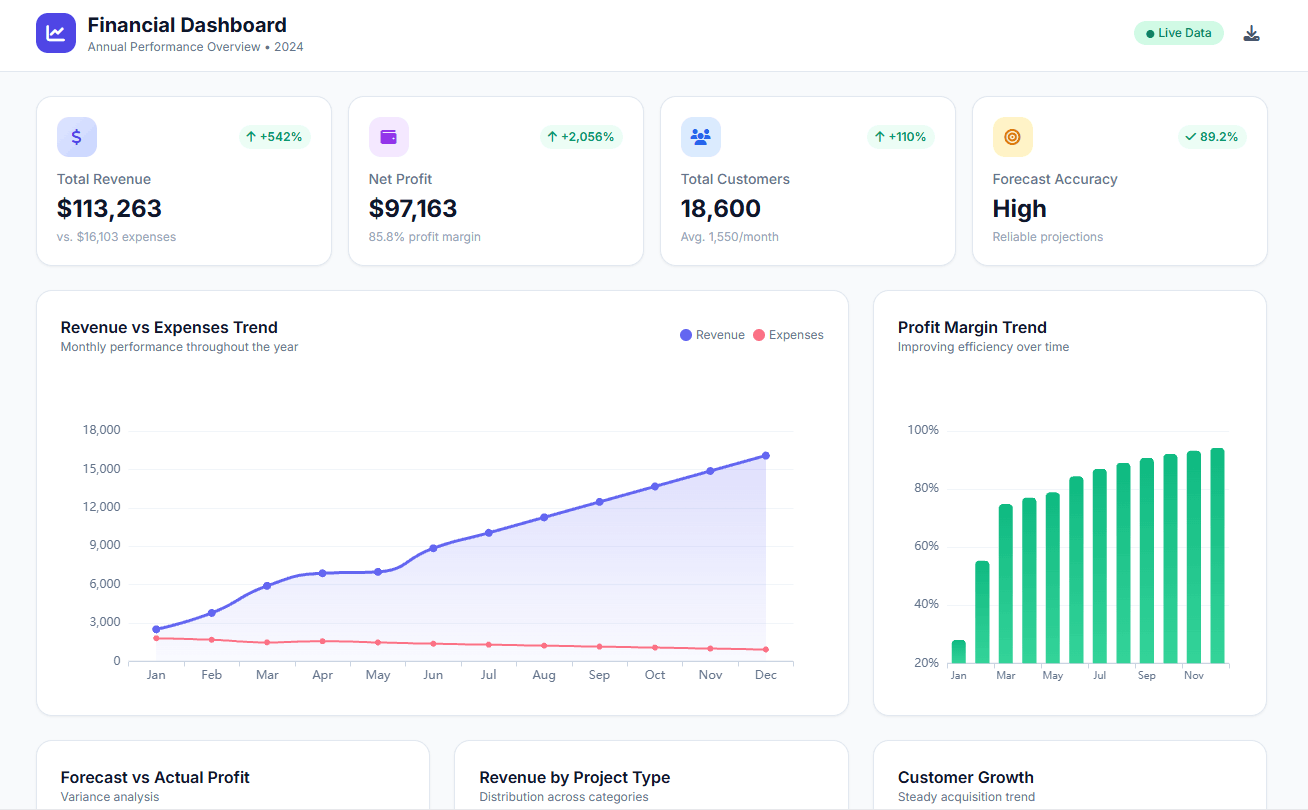
Set up dashboard & track KPIs
The debt to asset ratio calculator is a tool to assess a company’s financial health by indicating the proportion of its assets financed through debt. It’s essentially a measure of how leveraged a company is.
Calculate Debt To Asset Ratio
Debt-to-asset ratio formula
=Total Debt / Total Assets
Where,
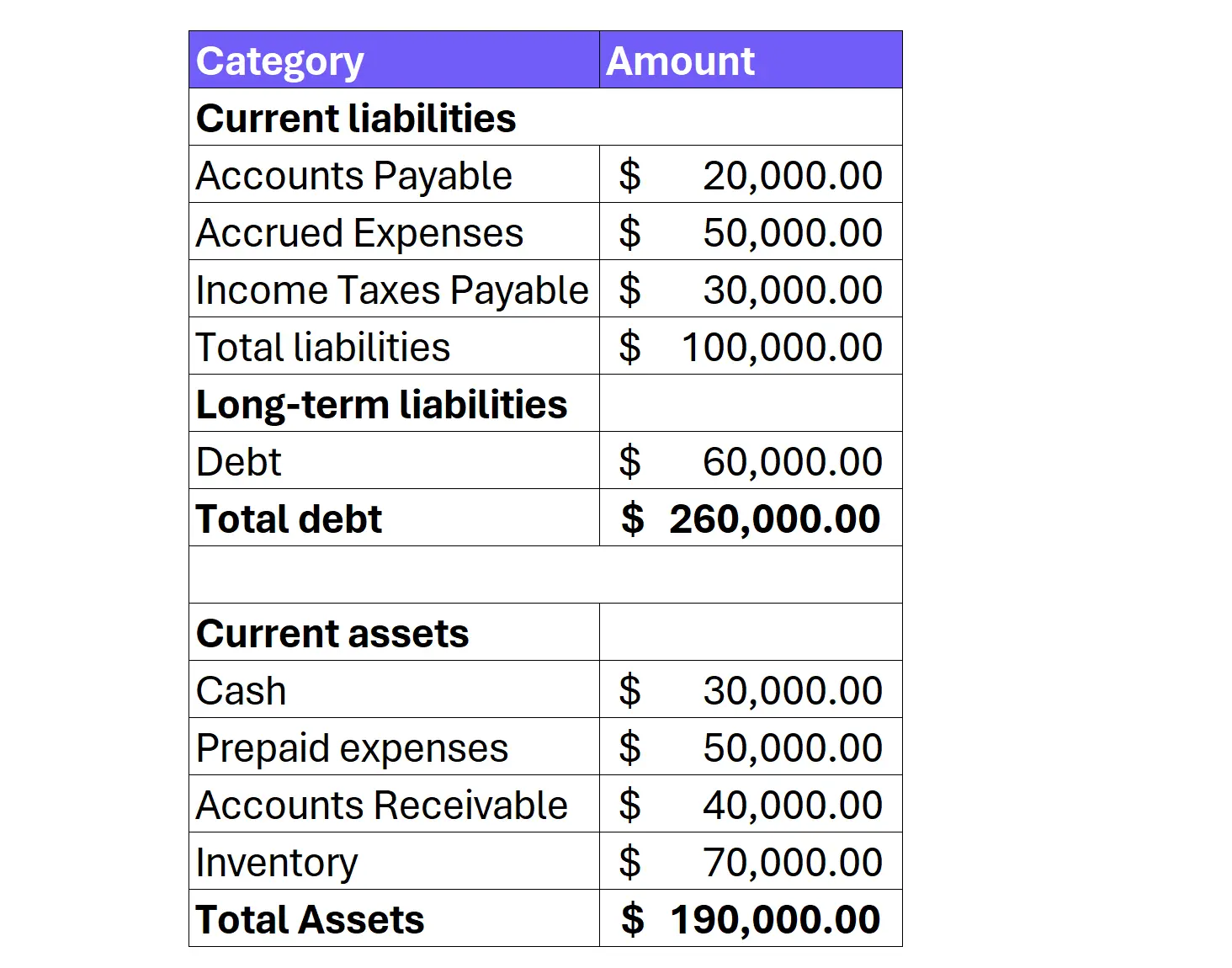
- Total Debt: Financial obligations that need to be repaid. It includes both current liabilities and long-term liabilities. This figure is on the company’s balance sheet under the “Liabilities” section.
- Total Assets: Everything a company owns that has economic value. It includes tangible assets like property, equipment, and inventory, as well as intangible assets like intellectual property and goodwill. The total assets figure can be found on the company’s balance sheet.
Struggling with manual calculations & tiring setups?
Let agentic AI do the heavy lifting.
Start free
Fast sign up & easy setup
How To Calculate Debt To Asset Ratio?
Time needed: 2 minutes
Step-by-step guide on how to calculate the debt-to-asset ratio:
- Find the Financial Statements
To get metrics you’ll need the company’s balance sheet.
- Identify Total Debt
On the balance sheet, locate the “Liabilities” section. This section will list all the company’s financial obligations. You’ll need to consider both current liabilities and long-term liabilities.
- Identify Total Assets
On the same balance sheet, locate the “Assets” section. This section lists everything the company owns that has economic value. It typically includes:
- Perform the Calculation
Once you have identified the total debt and total assets, simply divide the total debt by the total assets:
Debt-to-Asset Ratio = Total Debt / Total Assets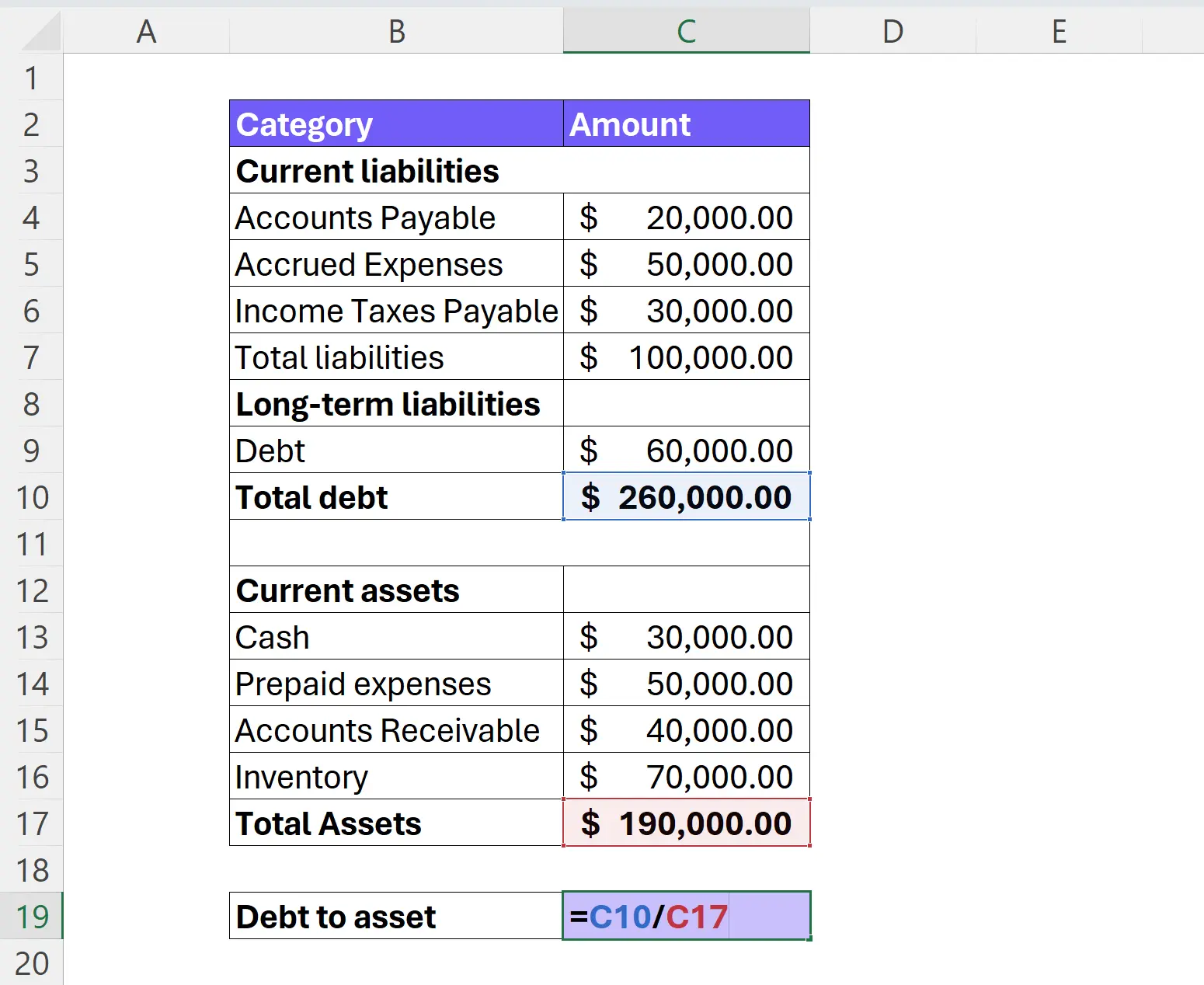
- Interpret the Ratio
A higher debt-to-asset ratio indicates a company has financed a larger portion of its assets with debt. This can be a sign of higher risk, as the company has more debt obligations to service. However, a lower ratio doesn’t necessarily mean better. Low ratio might suggest the company isn’t using debt strategically to grow.
Watch a video on how to calculate this ratio 👇
What is a good ratio?
There’s no single “good” debt-to-asset ratio that applies universally. It depends on several factors such as industry and company life stage. However, here’s a general guideline:
- A ratio below 1 (or 100%) generally indicates a company has more assets than debt, suggesting a more financially stable position.
- A ratio around 0.3 to 0.6 is where many investors feel comfortable, though this can vary depending on the company’s specific situation.
- A ratio above 2 might raise concerns about a company’s ability to manage its debt obligations, potentially indicating higher risk.

Infographic explaining what is a good debt-to-asset ratio, image by author
What are the limitations of this ratio?
- Asset Quality Blindness: It treats all assets equally, regardless of how easily they can be converted to cash (liquidity). A company with a large amount of inventory (illiquid) might have the same ratio as a company with a lot of cash (highly liquid) – but the second company is obviously in a better position.
- Debt Type Invisibility: The ratio doesn’t distinguish between different types of debt. Short-term, high-interest debt is riskier than long-term, low-interest debt. They both get lumped together in the calculation.
- Industry Benchmarks Needed: A high ratio in one industry might be normal, while a low ratio in another could be a sign of trouble. So it’s important to compare the ratio to industry benchmarks.
- Limited Future View: The ratio is a snapshot of a company’s financial health at a specific point. It doesn’t necessarily predict the future ability to repay debt.
Analysts use the debt-to-asset ratio alongside other metrics like liquidity and interest coverage ratios for a more complete financial picture. If one has too many debts, use a bankruptcy calculator to understand if bankruptcy might be a good option for you. Then seek professional advice on the best solutions for your situation.
Why measure debt to asset?
- Unlock company risk: Debt-to-asset ratio reveals how much debt a company finances its assets with. High ratio = potentially risky, low ratio = more stable.
- Spot smart growth: Young companies with decreasing debt-to-asset ratios might use debt strategically for growth.
- Assess your own finances: Calculate your debt-to-asset ratio to understand your financial leverage.
- Context is key: Ideal ratio varies by industry and company life stage.
FAQ
It varies greatly. Capital-intensive industries like manufacturing (lots of expensive equipment) tend to have much higher debt ratios than less capital-intensive ones like tech (which relies more on brainpower).
A high debt-to-asset ratio increases the risk of defaulting on loans and limits the ability to get new ones, making the company financially shakier.
Your debt-to-asset ratio is total liabilities divided by total assets. Find all you owe and own (car, house, savings). A lower ratio (more assets than debt) is generally better financially.
Other calculators
Setup and monitor your KPIs regularly using Ajelix BI