- Home
- Product
- Tools
- AI Data Analyst
- Excel Formula Generator
- Excel Formula Explainer
- Google Apps Script Generator
- Excel VBA Script Explainer
- AI VBA Code Generator
- Excel VBA Code Optimizer
- Excel VBA Code Debugger
- Google Sheets Formula Generator
- Google Apps Script Explainer
- Google Sheets Formula Explainer
- Google Apps Script Optimizer
- Google Apps Script Debugger
- AI Excel Spreadsheet Generator
- AI Excel Assistant
- AI Graph Generator
- Pricing
- Home
- Blog
- Calculators
- Free Return on Assets Calculator Online
Free Return on Assets Calculator Online

Explore other articles
- Google Sheets AI Agents That Autonomously Perform Tasks
- Advanced Agentic Research With AI Agents
- GLM-5 is Now Available on Ajelix AI Chat
- AI Spreadsheet Generator: Excel Templates With AI Agents
- Excel Financial Modeling With AI Agents (No Formulas Need!)
- AI Landing Page Generator: From 0 To Stunning Page With Agent
- Creating Charts In Excel with Agentic AI – It Does Everything!
- Create Report From Google Sheets Data with Agentic AI
- How To Create Powerpoint Presentation Using AI Agent (+Video)
- Ajelix Launches Agentic AI Chat That Executes Business Workflows, Not Just Conversation
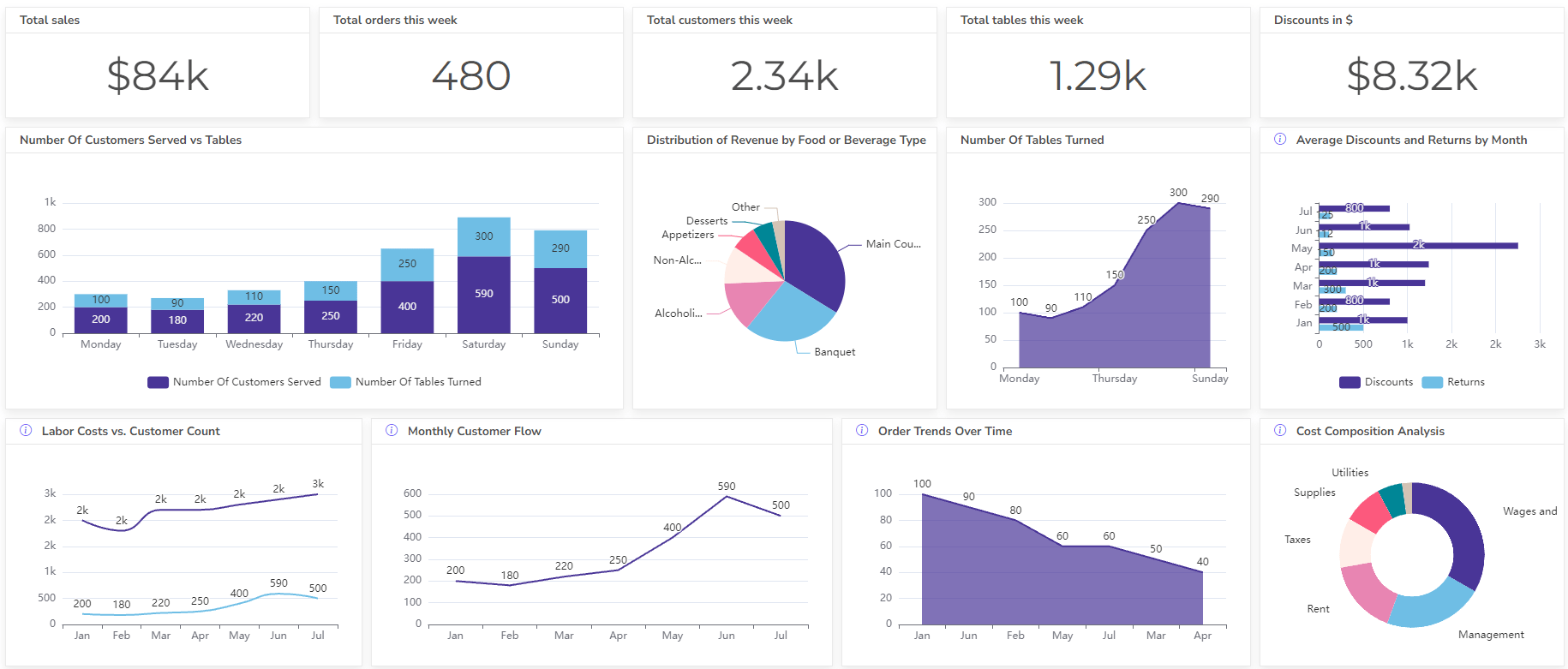
Set up dashboard & track KPIs
The Return on Assets calculator (ROA) is a financial metric used to assess a company’s profitability of total assets. This metric tells you how effectively your company uses resources (assets) to generate profit.
Calculate Return on Assets (ROA)
Return on Assets Formula
ROA = Net Income / Total Assets x 100
- Net Income: The profit earned after all expenses are paid.
- Total Assets: Total dollar value of everything the company owns.
What is a good Return Ratio?
A higher ROA is generally considered better, but a “good” ROA can vary depending on the industry. For example, an asset-heavy industry like manufacturing may have a naturally lower ratio than a service-based industry. It’s important to compare a company’s ROA to historical performance or industry benchmarks.
How To Calculate Return on Assets?
Time needed: 3 minutes
Step-by-step guide on how to calculate return on assets (ROA):
- Identify Net Income
Net income represents the company’s profit after all expenses have been paid. On the income statement, net income is usually the last line item.
- Identify Total Assets
Total assets represent the total dollar value of everything a company owns. This includes cash, inventory, property, equipment, and intangible assets like patents.
- Calculate the ROA Ratio
Once you have both figures, you can use the following formula to calculate ROA = Net Income / Total Assets x 100.
- Interpret the ROA
A higher ROA generally indicates better efficiency in using assets to generate profits. However, it’s important to consider industry benchmarks when interpreting ROA.
Difference between ROI and ROA
ROI and ROA are both financial metrics used to assess performance, but they measure different things:
- ROI (Return on Investment): Measures the profitability of a specific investment. It tells you how much return you get for your money on a particular project or venture.
- ROA (Return on Assets): Measures a company’s overall efficiency in using its assets to generate profit. It shows how well the company is squeezing profits out of everything it owns.
Here’s a table summarizing the key differences:
| Feature | ROI (Return on Investment) | ROA (Return on Assets) |
|---|---|---|
| What it Measures | Profitability of a specific investment | Overall efficiency in using assets |
| Focus | Return for a particular project | Company’s ability to generate profit from assets |
| Formula Typically Used | (Gain from Investment – Cost of Investment) / Cost of Investment | Net Income / Total Assets |
Why ROA Matters?
Financial metrics like Return on Assets are crucial for spotting strong investments. Here’s why ROA is a must-consider for your investment strategy:
- Efficiency Check: reveals how well a company uses its assets to generate profits. A high metric indicates efficient management and potentially, better returns for you.
- Industry Benchmarking: lets you compare companies within the same industry. This helps identify leaders in asset utilization.
- Tracking Performance: Monitoring this KPI for small businesses over time shows if a company’s management is improving efficiency.
- Potential Red Flags: A consistently low ROA, even compared to competitors, might signal underlying issues.
- Smarter Decisions: Use ROA alongside other metrics to make informed investment choices.
Other calculators
Setup and monitor your KPIs regularly using Ajelix BI